为了进行数据对象的版本控制,将mysql数据库中的表结构导出成文件进行版本化管理是非常重要的。以下是一个经过伪原创处理的python脚本,用于实现这一功能,同时保留了原来的功能和逻辑。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import pymysql
<p>class DatabaseManager:
connection = None
cursor = None</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false;"><code>def __init__(self, connection_params):
self.connection = pymysql.connect(
host=connection_params['host'],
port=connection_params['port'],
user=connection_params['user'],
passwd=connection_params['password'],
db=connection_params['db'],
charset=connection_params['charset']
)
self.cursor = self.connection.cursor()
def run_query(self, sql_string):
try:
with self.cursor as cursor:
cursor.execute(sql_string)
results = cursor.fetchall()
self.connection.close()
return results
except pymysql.Error as error:
print("MySQL query error:", error)
raise
def run_non_query(self, sql_string):
try:
with self.cursor as cursor:
cursor.execute(sql_string)
self.connection.commit()
self.connection.close()
except pymysql.Error as error:
print("MySQL non-query error:", error)
raisedef main():
connection_params = {
'host': '127.0.0.1',
'port': 3306,
'user': '**',
'password': '**',
'db': 'test',
'charset': 'utf8'
}
db_manager = DatabaseManager(connection_params)
sql_get_tables = "SELECT table_name FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = 'database_name';"
tables = db_manager.run_query(sql_get_tables)
<code># 定义文件目标路径,如果路径不存在,则创建
export_path = 'D:\mysqlscript'
if not os.path.exists(export_path):
os.mkdir(export_path)
mysqldump_params = {
'dump_command': 'mysqldump --no-data ',
'server': '127.0.0.1',
'user': '******',
'password': '******',
'port': 3306,
'db': 'database_name'
}
if tables:
for table in tables:
print(table[0])
os.chdir(export_path)
table_name = table[0]
export_file = f"{table_name}.sql"
sql_format = "%s -h%s -u%s -p%s -P%s %s %s >%s"
sql_command = sql_format % (
mysqldump_params['dump_command'],
mysqldump_params['server'],
mysqldump_params['user'],
mysqldump_params['password'],
mysqldump_params['port'],
mysqldump_params['db'],
table_name,
export_file
)
print(sql_command)
result = os.system(sql_command)
if result == 0:
print('导出成功')
else:
print('导出失败')</code>if name == 'main': main()
数据库测试脚本:
CREATE DATABASE test_database CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_bin;</p><p>USE test_database;</p><p>CREATE TABLE table_a (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE,
create_date DATETIME,
PRIMARY KEY pk_id(id),
INDEX idx_create_date(create_date)
);</p><p>INSERT INTO table_a (name, create_date) VALUES ('aaaaaa', NOW());
INSERT INTO table_a (name, create_date) VALUES ('bbbbbb', NOW());</p><p>CREATE TABLE table_b (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE,
create_date DATETIME,
PRIMARY KEY pk_id(id),
INDEX idx_create_date(create_date)
);</p><p>INSERT INTO table_b (name, create_date) VALUES ('aaaaaa', NOW());
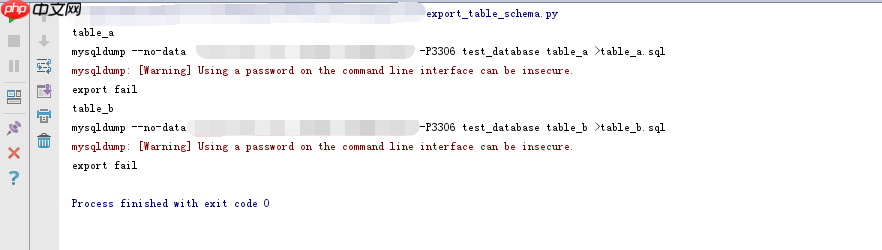
INSERT INTO table_b (name, create_date) VALUES ('bbbbbb', NOW());执行脚本时可能会出现以下警告,但这不会影响最终结果:
<code>mysqldump: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.</code>
立即学习“Python免费学习笔记(深入)”;
请注意,mysqldump导出的表结构可能会根据表的数据情况对自增列进行编号。这是mysqldump工具本身的问题,如果需要,可以进行相应的修改。
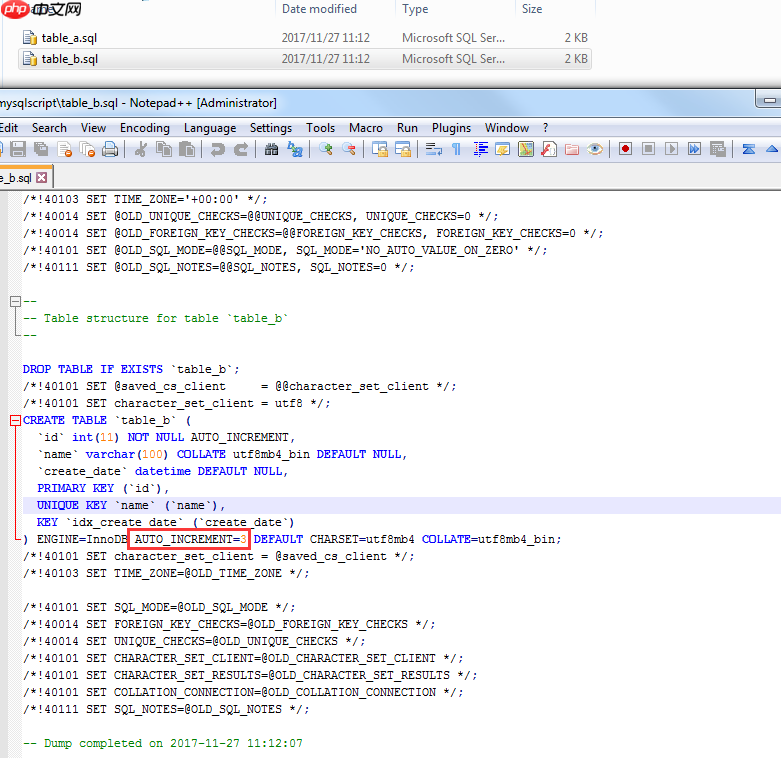
移除mysqldump导出表结构中的注释信息:
import os</p><p>export_path = "D:mysqlscript"
os.chdir(export_path)
files = os.listdir(export_path)
for file in files:
with open(file, "r") as f:
content = "USE **<em>;
"
for line in f:
if not (line.startswith("--") or line.startswith("/</em>")):
if line != "
" and line.startswith(") ENGINE"):
content += "
" + ")"
else:
content += line
print(content)
with open(file, 'w') as f:
f.write(content)通过以上脚本,您可以轻松地将MySQL数据库中的表结构导出到文件中,并进行版本控制管理。
以上就是Python导出MySQL数据库中表的建表语句到文件的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号