大家好,很高兴再次与大家见面,我是你们的老朋友全栈君。
Java PreparedStatement与Statement类似,是Java JDBC Framework的一部分。它用于对数据库执行CRUD操作。PreparedStatement扩展了Statement接口。由于支持参数化查询,PreparedStatement被认为更为安全,并且可以防止SQL注入攻击。我们可以通过调用Connection的prepareStatement(String query)方法来获取PreparedStatement的实例,如下所示:
// 方法:public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String query) throws SQLException {}
// 使用:Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customerdb", "root", "root");
PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement("select id, firstname, lastname, email, birthdate from tblcustomer");PreparedStatement的优势:
PreparedStatement不仅可以用于参数化查询,还可以用于普通查询。其查询性能优于Statement。PreparedStatement的实例可以被重复使用,以执行具有不同参数的同一查询。此外,PreparedStatement可以保护应用程序免受SQL注入攻击。
立即学习“Java免费学习笔记(深入)”;
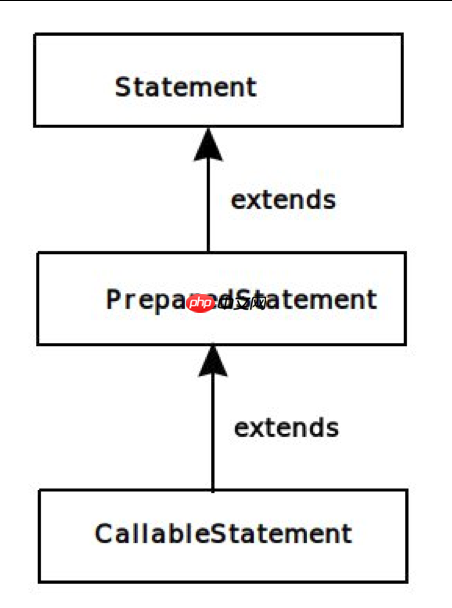
Java PreparedStatement层次结构
PreparedStatement方法:
我们可以将方法分为不同的类别。
执行查询:
ResultSet executeQuery():此方法用于通过PreparedStatement对象执行读取操作,返回ResultSet实例以获取数据。int executeUpdate():此方法用于执行插入、删除和更新查询,返回一个整数值,表示受查询影响的数据库行数。将参数值传递给查询:
void setInt(int parameterIndex, int value):将Integer值设置为指定的参数索引。void setShort(int parameterIndex, short value):将short值设置为指定的参数索引。void setLong(int parameterIndex, long value):将Long值设置为指定的参数索引。void setFloat(int parameterIndex, float value):将Float值设置为指定的参数索引。void setDouble(int parameterIndex, double value):将Double值设置为指定的参数索引。void setBigDecimal(int parameterIndex, BigDecimal value):将BigDecimal值设置为指定的参数索引。void setString(int parameterIndex, String value):将String值设置为指定的参数索引。void setDate(int parameterIndex, Date value):将Date值设置为指定的参数索引。注意:参数索引值从1开始,所有这些方法都会抛出SQLException。
Java PreparedStatement示例:
我们将使用MySQL数据库来演示PreparedStatement的使用。使用以下DB脚本创建数据库、表和示例数据:
create database customerdb;
use customerdb;
create table tblcustomer(
id integer AUTO_INCREMENT primary key,
firstname varchar(32),
lastname varchar(32),
email varchar(32),
birthdate datetime);
insert into tblcustomer (id,firstname,lastname,email,birthdate) values(1,'Ricky','Smith','ricky@google.com','2001-12-10');数据库连接信息:
Maven依赖关系:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.48</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>使用PreparedStatement获取数据:
在这种情况下,我们将从tblcustomer表中获取具有指定id的行。查询将返回单行。
package com.journaldev.examples;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
public class PreparedStatementDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
int customerId = 1;
String query = "select id, firstname, lastname, email, birthdate from tblcustomer where id = ?";
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customerdb", "root", "root");
ps = con.prepareStatement(query);
ps.setInt(1, customerId);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println("Id:" + rs.getInt(1));
System.out.println("First Name:" + rs.getString(2));
System.out.println("Last Name:" + rs.getString("lastname"));
System.out.println("Email:" + rs.getString("email"));
System.out.println("BirthDate:" + rs.getDate("birthdate"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
rs.close();
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}
}执行步骤:
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver") 将JDBC驱动程序加载到内存中。DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customerdb", "root", "root");PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement("select id, firstname, lastname, email, birthdate from tblcustomer");int customerId = 1;ps.setInt(1, customerId); setInt(,)方法有两个参数。在上面的示例中,“1”是参数编号,变量customerId是参数的值。executeQuery()方法用于执行选择查询。它将返回ResultSet的实例。如果查询用于插入、更新或删除,则可以使用executeUpdate()。next()方法用于获取查询输出。程序输出:
Id:1 First Name:Ricky Last Name:Smith Email:ricky@google.com BirthDate:2001-12-1
使用PreparedStatement进行插入操作:
在此示例中,我们将使用PreparedStatement在tblcustomer表中执行插入操作。
package com.journaldev.examples;
import java.sql.*;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class PrepareStatementInsertDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
String firstname = "matthew";
String lastname = "wade";
String email = "matthew@java.com";
Date birthdate = new Date(new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD").parse("2000-12-12").getTime());
String query = "insert into tblcustomer (id,firstname,lastname,email,birthdate) values(default,?,?,?,?)";
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customerdb", "root", "root");
ps = con.prepareStatement(query, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
ps.setString(1, firstname);
ps.setString(2, lastname);
ps.setString(3, email);
ps.setDate(4, birthdate);
int row = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("No. of Rows inserted:" + row);
rs = ps.getGeneratedKeys();
if (rs.next()) {
System.out.println("Id of new Customer:" + rs.getInt(1));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
rs.close();
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}
}在此示例中,在创建PreparedStatement实例时,我们传递了两个参数。第一个是查询本身,第二个是“Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS”,这将帮助我们获取新行的主键值。
以下代码用于为插入查询提供参数:
ps.setString(1, firstname); ps.setString(2, lastname); ps.setString(3, email); ps.setDate(4, birthdate);
如前面的程序中所述,executeUpdate()方法用于执行插入操作。它将返回受我们的查询影响的行数。
程序输出:
No. of Rows inserted:1 Id of new Customer:2
如果您转到数据库并执行选择查询,您将看到以下结果:
mysql> use customerdb; Database changed mysql> select * from tblcustomer; +----+-----------+----------+------------------+---------------------+ | id | firstname | lastname | email | birthdate | +----+-----------+----------+------------------+---------------------+ | 1 | Ricky | Smith | ricky@google.com | 2001-12-10 00:00:00 | | 2 | matthew | wade | matthew@java.com | 1999-12-26 00:00:00 | +----+-----------+----------+------------------+---------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
使用PreparedStatement进行更新操作:
现在我们将执行更新操作。我们将更新电子邮件为“matthew@java.com”的客户的名字和姓氏。这行是在前面的示例中插入的。
package com.journaldev.examples;
import java.sql.*;
public class PrepareStatementUpdateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
String email = "matthew@java.com";
String newFirstname = "john";
String newLastname = "smith";
String query = "update tblcustomer set firstname = ?,lastname =? where email = ?";
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customerdb", "root", "root");
ps = con.prepareStatement(query);
ps.setString(1, newFirstname);
ps.setString(2, newLastname);
ps.setString(3, email);
int row = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("No. of Rows Updated:" + row);
if (row == 1) {
String selectQuery = "select id,firstname,lastname,email,birthdate from tblcustomer where email=?";
try (PreparedStatement selStatement = con.prepareStatement(selectQuery);) {
selStatement.setString(1, email);
ResultSet rs = selStatement.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
System.out.println("Id:" + rs.getInt(1));
System.out.println("First Name:" + rs.getString(2));
System.out.println("Last Name:" + rs.getString("lastname"));
System.out.println("Email:" + rs.getString("email"));
System.out.println("BirthDate:" + rs.getDate("birthdate"));
}
rs.close();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}
}了解程序:
在上面的示例中,我们在查询中有三个参数。第一个是新名字,第二个是新姓氏,第三个是客户的电子邮件。
以下代码行将此参数的值提供给PreparedStatement:
ps.setString(1, newFirstname); ps.setString(2, newLastname); ps.setString(3, email);
executeUpdate()方法用于执行更新查询。它将返回查询更新的行数。
程序输出:
No. of Rows Updated:1 Id:2 First Name:john Last Name:smith Email:matthew@java.com BirthDate:1999-12-26
您可以使用SQL查询在数据库中检查更新:
mysql> select * from tblcustomer; +----+-----------+----------+------------------+---------------------+ | id | firstname | lastname | email | birthdate | +----+-----------+----------+------------------+---------------------+ | 1 | Ricky | Smith | ricky@google.com | 2001-12-10 00:00:00 | | 2 | john | smith | matthew@java.com | 1999-12-26 00:00:00 | +----+-----------+----------+------------------+---------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
使用PreparedStatement进行删除操作:
现在我们将删除电子邮件为“matthew@java.com”的客户记录。
package com.journaldev.examples;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class PrepareStatementDeleteDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
String email = "matthew@java.com";
String query = "delete from tblcustomer where email = ?";
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customerdb", "root", "root");
ps = con.prepareStatement(query);
ps.setString(1, email);
int row = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("No. of Rows Deleted:" + row);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}
}PreparedStatement中的批处理方法:
void addBatch():此方法用于将参数集添加到此PreparedStatement对象的批处理中,以更新多行。int[] executeBatch():此方法从PreparedStatement对象的批处理中执行所有SQL查询,并返回更新计数数组。如果此方法无法执行,并且JDBC驱动程序可能会也可能不会继续处理剩余的批处理,则会抛出BatchUpdateException。使用PreparedStatement的批量/批量操作:
package com.journaldev.examples;
import java.sql.*;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class PrepareStatementBatchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD");
String query = "insert into tblcustomer (id,firstname,lastname,email,birthdate) values(default,?,?,?,?)";
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customerdb", "root", "root");
ps = con.prepareStatement(query, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
// 1st Insert
ps.setString(1, "Ross");
ps.setString(2, "Southee");
ps.setString(3, "ross@java.com");
ps.setDate(4, new Date(sdf.parse("2000-12-12").getTime()));
ps.addBatch();
// 2nd Insert
ps.setString(1, "Mayank");
ps.setString(2, "Kohli");
ps.setString(3, "mayank@java.com");
ps.setDate(4, new Date(sdf.parse("2005-12-12").getTime()));
ps.addBatch();
// 3rd Insert
ps.setString(1, "Tom");
ps.setString(2, "Patel");
ps.setString(3, "tom@java.com");
ps.setDate(4, new Date(sdf.parse("1995-12-12").getTime()));
ps.addBatch();
// Execution
int[] rows = ps.executeBatch();
for (int row : rows) {
System.out.println("No. of Rows inserted:" + row);
}
rs = ps.getGeneratedKeys();
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println("Id of new Customer:" + rs.getInt(1));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
rs.close();
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}
}在上面的示例中,我们分批插入了3个客户记录。批量插入多行比单行插入更有效。addBatch()方法将数据添加到批处理中。executeBatch()执行批处理中的所有查询。
输出:
No. of Rows inserted:1 No. of Rows inserted:1 No. of Rows inserted:1 Id of new Customer:10 Id of new Customer:11 Id of new Customer:12
您可以通过此链接下载完整的Java项目。
参考:Java文档
发布者:全栈程序员栈长,转载请注明出处:https://www.php.cn/link/dbe2b7e940f999dbd70a13eb1da19ea1 原文链接:https://www.php.cn/link/c8377ad2a50fb65de28b11cfc628d75c
以上就是Java PreparedStatement的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号