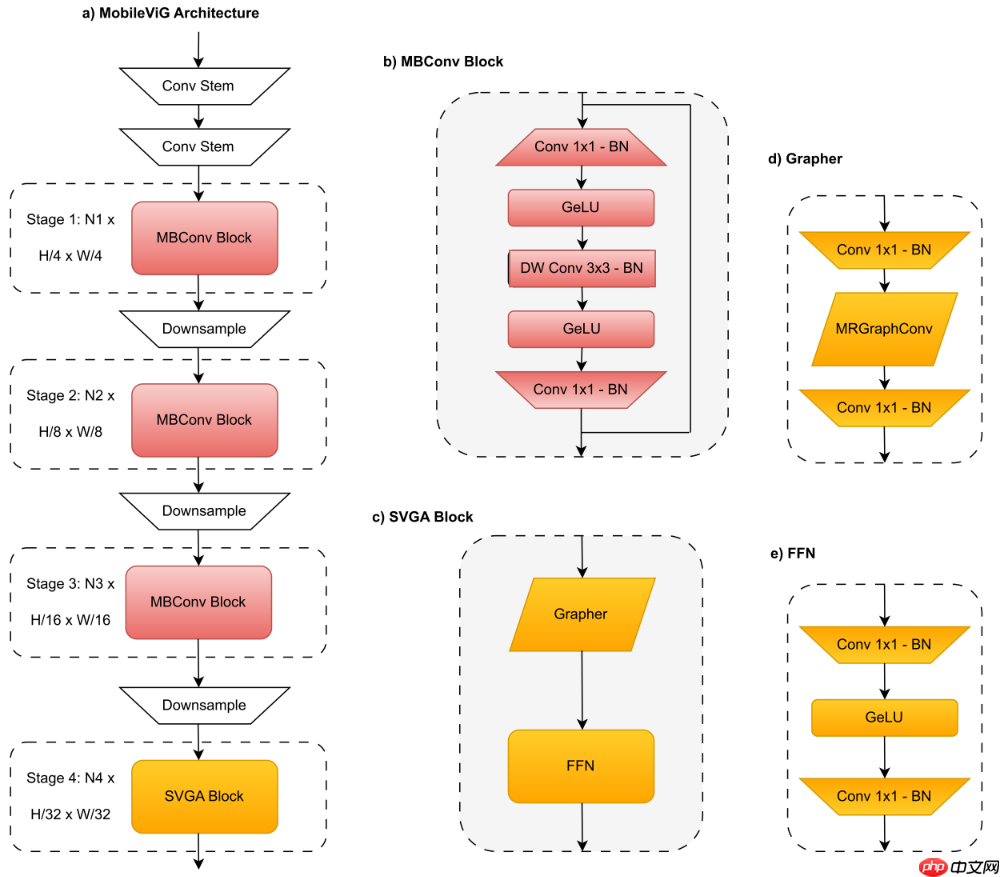
该代码复现了MobileViG模型,这是一种混合CNN-GNN架构。代码先下载导入库,创建并处理Cifar10数据集,接着实现标签平滑、DropPath等组件,构建Stem、MLP等模块及MobileViG模型,还定义了不同规模模型。之后进行训练、结果分析,包括绘制学习曲线、计算吞吐量和展示预测结果等。
☞☞☞AI 智能聊天, 问答助手, AI 智能搜索, 免费无限量使用 DeepSeek R1 模型☜☜☜

传统上,卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉变换器(ViT)主导了计算机视觉。 然而,最近提出的视觉图神经网络(ViG)提供了一种新的探索途径。 不幸的是,对于移动应用程序来说,由于将图像表示为图形结构的开销,ViG 的计算成本很高。 在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的基于图的稀疏注意力机制,即稀疏视觉图注意力(SVGA),它是为在移动设备上运行的 ViG 设计的。 此外,我们提出了第一个用于移动设备视觉任务的混合 CNN-GNN 架构 MobileViG,它使用 SVGA。 大量实验表明,MobileViG 在图像分类、对象检测和实例分割任务的准确性和/或速度方面击败了现有的 ViG 模型以及现有的移动 CNN 和 ViT 架构。 我们最快的模型 MobileViG-Ti 在 ImageNet-1K 上实现了 75.7% 的 top-1 准确率,在 iPhone 13 Mini NPU(用 CoreML 编译)上的推理延迟为 0.78 毫秒,这比 MobileNetV2x1.4 更快(1.02 毫秒,74.7% top-1) 1) 和 MobileNetV2x1.0(0.81 毫秒,71.8% top-1)。 我们最大的模型 MobileViG-B 获得了 82.6% 的 top-1 准确率,延迟仅为 2.30 毫秒,比类似大小的 EfficientFormer-L3 模型(2.77 毫秒,82.4%)更快、更准确。 我们的工作证明,精心设计的混合 CNN-GNN 架构可以成为设计在移动设备上极其快速和准确的模型的新探索途径。
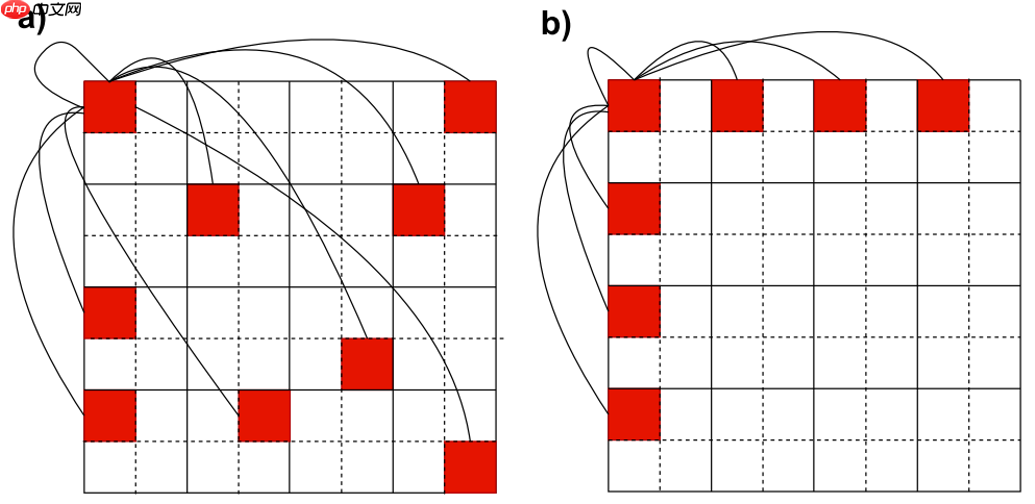
基于 KNN 的图注意力引入了两个不适合移动设备的组件:KNN 计算和输入整形,本文用 SVGA 删除了它们,并沿行和列跨k个Token进行采样,从而构建图来进行学习。为了避免reshape带来的开销,本文提出通过滑动操作来进行图学习,具体实现如算法1所示。
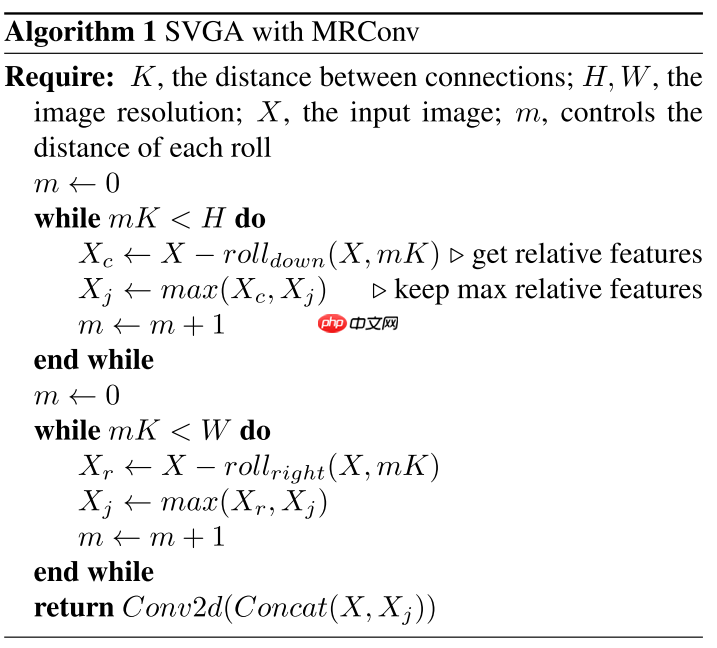
跟传统的Transformer架构差不多,SVGA Block分为两个部分:Grapher和FFN
%matplotlib inlineimport paddleimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom paddle.vision.datasets import Cifar10from paddle.vision.transforms import Transposefrom paddle.io import Dataset, DataLoaderfrom paddle import nnimport paddle.nn.functional as Fimport paddle.vision.transforms as transformsimport osimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom matplotlib.pyplot import figure
train_tfm = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224, scale=(0.6, 1.0)),
transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.2,contrast=0.2, saturation=0.2),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(0.5),
transforms.RandomRotation(20),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)),
])
test_tfm = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)),
])paddle.vision.set_image_backend('cv2')# 使用Cifar10数据集train_dataset = Cifar10(data_file='data/data152754/cifar-10-python.tar.gz', mode='train', transform = train_tfm, )
val_dataset = Cifar10(data_file='data/data152754/cifar-10-python.tar.gz', mode='test',transform = test_tfm)print("train_dataset: %d" % len(train_dataset))print("val_dataset: %d" % len(val_dataset))train_dataset: 50000 val_dataset: 10000
batch_size=256
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, drop_last=True, num_workers=4) val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, drop_last=False, num_workers=4)
class LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, smoothing=0.1):
super().__init__()
self.smoothing = smoothing def forward(self, pred, target):
confidence = 1. - self.smoothing
log_probs = F.log_softmax(pred, axis=-1)
idx = paddle.stack([paddle.arange(log_probs.shape[0]), target], axis=1)
nll_loss = paddle.gather_nd(-log_probs, index=idx)
smooth_loss = paddle.mean(-log_probs, axis=-1)
loss = confidence * nll_loss + self.smoothing * smooth_loss return loss.mean()def drop_path(x, drop_prob=0.0, training=False):
"""
Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
the original name is misleading as 'Drop Connect' is a different form of dropout in a separate paper...
See discussion: https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/issues/494#issuecomment-532968956 ...
"""
if drop_prob == 0.0 or not training: return x
keep_prob = paddle.to_tensor(1 - drop_prob)
shape = (paddle.shape(x)[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1)
random_tensor = keep_prob + paddle.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype)
random_tensor = paddle.floor(random_tensor) # binarize
output = x.divide(keep_prob) * random_tensor return outputclass DropPath(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, drop_prob=None):
super(DropPath, self).__init__()
self.drop_prob = drop_prob def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)class Stem(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim, activation=nn.GELU):
super(Stem, self).__init__()
self.stem = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2D(input_dim, output_dim // 2, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm2D(output_dim // 2),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Conv2D(output_dim // 2, output_dim, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm2D(output_dim),
nn.GELU()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.stem(x)class MLP(nn.Layer):
"""
Implementation of MLP with 1*1 convolutions.
Input: tensor with shape [B, C, H, W]
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None,
out_features=None, drop=0., mid_conv=False):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.mid_conv = mid_conv
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2D(in_features, hidden_features, 1, bias_attr=False)
self.act = nn.GELU()
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2D(hidden_features, out_features, 1, bias_attr=False)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop) if self.mid_conv:
self.mid = nn.Conv2D(hidden_features, hidden_features, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
groups=hidden_features, bias_attr=False)
self.mid_norm = nn.BatchNorm2D(hidden_features)
self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2D(hidden_features)
self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2D(out_features) def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.norm1(x)
x = self.act(x) if self.mid_conv:
x_mid = self.mid(x)
x_mid = self.mid_norm(x_mid)
x = self.act(x_mid)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.norm2(x)
x = self.drop(x) return xclass InvertedResidual(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, dim, mlp_ratio=4., drop=0., drop_path=0., use_layer_scale=True, layer_scale_init_value=1e-5):
super().__init__()
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = MLP(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, drop=drop, mid_conv=True)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. \ else nn.Identity()
self.use_layer_scale = use_layer_scale if use_layer_scale:
self.layer_scale_2 = self.create_parameter(shape=(1, dim, 1, 1), default_initializer=nn.initializer.Constant(layer_scale_init_value)) def forward(self, x):
if self.use_layer_scale:
x = x + self.drop_path(self.layer_scale_2 * self.mlp(x)) else:
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(x)) return xclass MRConv4D(nn.Layer):
"""
Max-Relative Graph Convolution (Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.03751) for dense data type
K is the number of superpatches, therefore hops equals res // K.
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, K=2):
super(MRConv4D, self).__init__()
self.nn = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2D(in_channels * 2, out_channels, 1, bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm2D(in_channels * 2),
nn.GELU()
)
self.K = K def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
x_j = x - x for i in range(self.K, H, self.K):
x_c = x - paddle.concat([x[:, :, -i:, :], x[:, :, :-i, :]], axis=2)
x_j = paddle.maximum(x_j, x_c) for i in range(self.K, W, self.K):
x_r = x - paddle.concat([x[:, :, :, -i:], x[:, :, :, :-i]], axis=3)
x_j = paddle.maximum(x_j, x_r)
x = paddle.concat([x, x_j], axis=1) return self.nn(x)class Grapher(nn.Layer):
"""
Grapher module with graph convolution and fc layers
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, drop_path=0.0, K=2):
super(Grapher, self).__init__()
self.channels = in_channels
self.K = K
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2D(in_channels, in_channels, 1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2D(in_channels),
)
self.graph_conv = MRConv4D(in_channels, in_channels * 2, K=self.K)
self.fc2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2D(in_channels * 2, in_channels, 1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2D(in_channels),
)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
_tmp = x
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.graph_conv(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop_path(x) + _tmp return xclass Downsample(nn.Layer):
""" Convolution-based downsample
"""
def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2D(in_dim, out_dim, 3, stride=2, padding=1, bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm2D(out_dim),
) def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x) return xclass FFN(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, drop_path=0.0):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features # same as input
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features # x4
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2D(in_features, hidden_features, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm2D(hidden_features),
)
self.act = nn.GELU()
self.fc2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2D(hidden_features, out_features, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm2D(out_features),
)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity() def forward(self, x):
shortcut = x
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop_path(x) + shortcut return xclass MobileViG(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, local_blocks, local_channels,
global_blocks, global_channels,
dropout=0., drop_path=0., emb_dims=512,
K=2, distillation=True, num_classes=1000):
super(MobileViG, self).__init__()
self.distillation = distillation
n_blocks = sum(global_blocks) + sum(local_blocks)
dpr = [x.item() for x in paddle.linspace(0, drop_path, n_blocks)] # stochastic depth decay rule
dpr_idx = 0
self.stem = Stem(input_dim=3, output_dim=local_channels[0])
# local processing with inverted residuals
self.local_backbone = nn.LayerList([]) for i in range(len(local_blocks)): if i > 0:
self.local_backbone.append(Downsample(local_channels[i-1], local_channels[i])) for _ in range(local_blocks[i]):
self.local_backbone.append(InvertedResidual(dim=local_channels[i], mlp_ratio=4, drop_path=dpr[dpr_idx]))
dpr_idx += 1
self.local_backbone.append(Downsample(local_channels[-1], global_channels[0])) # transition from local to global
# global processing with svga
self.backbone = nn.LayerList([]) for i in range(len(global_blocks)): if i > 0:
self.backbone.append(Downsample(global_channels[i-1], global_channels[i])) for j in range(global_blocks[i]):
self.backbone.append(nn.Sequential(
Grapher(global_channels[i], drop_path=dpr[dpr_idx], K=K),
FFN(global_channels[i], global_channels[i] * 4, drop_path=dpr[dpr_idx])
)
)
dpr_idx += 1
self.prediction = nn.Sequential(nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2D(1),
nn.Conv2D(global_channels[-1], emb_dims, 1, bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm2D(emb_dims),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout))
self.head = nn.Conv2D(emb_dims, num_classes, 1, bias_attr=True)
if self.distillation:
self.dist_head = nn.Conv2D(emb_dims, num_classes, 1, bias_attr=True)
self.apply(self._init_weights) def _init_weights(self, m):
tn = nn.initializer.TruncatedNormal(std=.02)
km = nn.initializer.KaimingNormal()
one = nn.initializer.Constant(1.0)
zero = nn.initializer.Constant(0.0) if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
tn(m.weight) if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
zero(m.bias) elif isinstance(m, (nn.LayerNorm, nn.BatchNorm2D)):
zero(m.bias)
one(m.weight) elif isinstance(m, nn.Conv2D):
km(m.weight) if m.bias is not None:
zero(m.bias) def forward(self, inputs):
x = self.stem(inputs)
B, C, H, W = x.shape for i in range(len(self.local_backbone)):
x = self.local_backbone[i](x) for i in range(len(self.backbone)):
x = self.backbone[i](x)
x = self.prediction(x)
if self.distillation:
x = self.head(x).squeeze(-1).squeeze(-1), self.dist_head(x).squeeze(-1).squeeze(-1) if not self.training:
x = (x[0] + x[1]) / 2
else:
x = self.head(x).squeeze(-1).squeeze(-1) return xnum_classes = 10def mobilevig_ti(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model = MobileViG(local_blocks=[2, 2, 6],
local_channels=[42, 84, 168],
global_blocks=[2],
global_channels=[256],
dropout=0.,
drop_path=0.1,
emb_dims=512,
K=2,
distillation=False,
num_classes=num_classes) return modeldef mobilevig_s(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model = MobileViG(local_blocks=[3, 3, 9],
local_channels=[42, 84, 176],
global_blocks=[3],
global_channels=[256],
dropout=0.,
drop_path=0.1,
emb_dims=512,
K=2,
distillation=False,
num_classes=num_classes) return modeldef mobilevig_m(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model = MobileViG(local_blocks=[3, 3, 9],
local_channels=[42, 84, 224],
global_blocks=[3],
global_channels=[400],
dropout=0.,
drop_path=0.1,
emb_dims=768,
K=2,
distillation=False,
num_classes=num_classes) return modeldef mobilevig_b(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model = MobileViG(local_blocks=[5, 5, 15],
local_channels=[42, 84, 240],
global_blocks=[5],
global_channels=[464],
dropout=0.,
drop_path=0.1,
emb_dims=768,
K=2,
distillation=False,
num_classes=num_classes) return modelmodel = mobilevig_ti() paddle.summary(model, (1, 3, 224, 224))
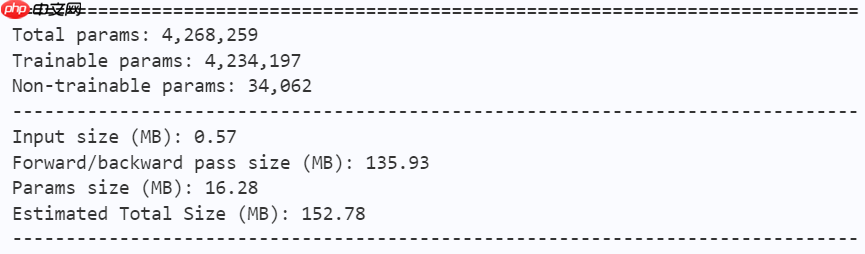
model = mobilevig_s() paddle.summary(model, (1, 3, 224, 224))
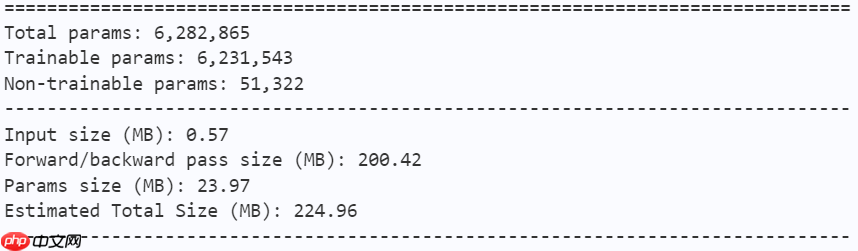
model = mobilevig_m() paddle.summary(model, (1, 3, 224, 224))
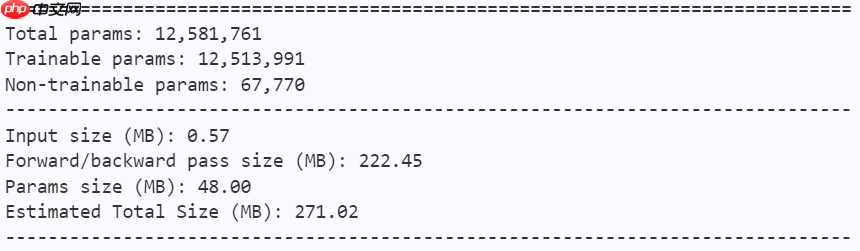
model = mobilevig_b() paddle.summary(model, (1, 3, 224, 224))
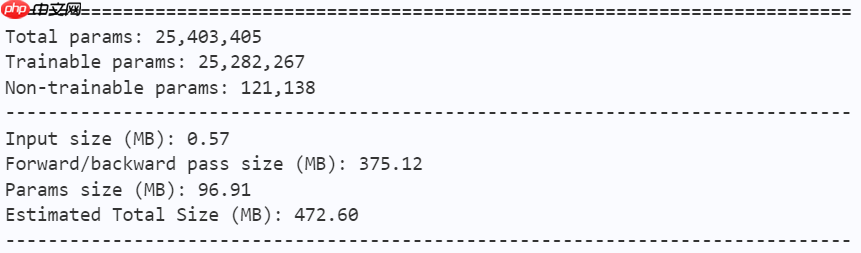
learning_rate = 0.001n_epochs = 100paddle.seed(42) np.random.seed(42)
work_path = 'work/model'# MobileViG-Tinymodel = mobilevig_ti()
criterion = LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy()
scheduler = paddle.optimizer.lr.CosineAnnealingDecay(learning_rate=learning_rate, T_max=50000 // batch_size * n_epochs, verbose=False)
optimizer = paddle.optimizer.Adam(parameters=model.parameters(), learning_rate=scheduler, weight_decay=1e-5)
gate = 0.0threshold = 0.0best_acc = 0.0val_acc = 0.0loss_record = {'train': {'loss': [], 'iter': []}, 'val': {'loss': [], 'iter': []}} # for recording lossacc_record = {'train': {'acc': [], 'iter': []}, 'val': {'acc': [], 'iter': []}} # for recording accuracyloss_iter = 0acc_iter = 0for epoch in range(n_epochs): # ---------- Training ----------
model.train()
train_num = 0.0
train_loss = 0.0
val_num = 0.0
val_loss = 0.0
accuracy_manager = paddle.metric.Accuracy()
val_accuracy_manager = paddle.metric.Accuracy() print("#===epoch: {}, lr={:.10f}===#".format(epoch, optimizer.get_lr())) for batch_id, data in enumerate(train_loader):
x_data, y_data = data
labels = paddle.unsqueeze(y_data, axis=1)
logits = model(x_data)
loss = criterion(logits, y_data)
acc = accuracy_manager.compute(logits, labels)
accuracy_manager.update(acc) if batch_id % 10 == 0:
loss_record['train']['loss'].append(loss.numpy())
loss_record['train']['iter'].append(loss_iter)
loss_iter += 1
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
optimizer.clear_grad()
train_loss += loss
train_num += len(y_data)
total_train_loss = (train_loss / train_num) * batch_size
train_acc = accuracy_manager.accumulate()
acc_record['train']['acc'].append(train_acc)
acc_record['train']['iter'].append(acc_iter)
acc_iter += 1
# Print the information.
print("#===epoch: {}, train loss is: {}, train acc is: {:2.2f}%===#".format(epoch, total_train_loss.numpy(), train_acc*100)) # ---------- Validation ----------
model.eval() for batch_id, data in enumerate(val_loader):
x_data, y_data = data
labels = paddle.unsqueeze(y_data, axis=1) with paddle.no_grad():
logits = model(x_data)
loss = criterion(logits, y_data)
acc = val_accuracy_manager.compute(logits, labels)
val_accuracy_manager.update(acc)
val_loss += loss
val_num += len(y_data)
total_val_loss = (val_loss / val_num) * batch_size
loss_record['val']['loss'].append(total_val_loss.numpy())
loss_record['val']['iter'].append(loss_iter)
val_acc = val_accuracy_manager.accumulate()
acc_record['val']['acc'].append(val_acc)
acc_record['val']['iter'].append(acc_iter)
print("#===epoch: {}, val loss is: {}, val acc is: {:2.2f}%===#".format(epoch, total_val_loss.numpy(), val_acc*100)) # ===================save====================
if val_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = val_acc
paddle.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(work_path, 'best_model.pdparams'))
paddle.save(optimizer.state_dict(), os.path.join(work_path, 'best_optimizer.pdopt'))print(best_acc)
paddle.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(work_path, 'final_model.pdparams'))
paddle.save(optimizer.state_dict(), os.path.join(work_path, 'final_optimizer.pdopt'))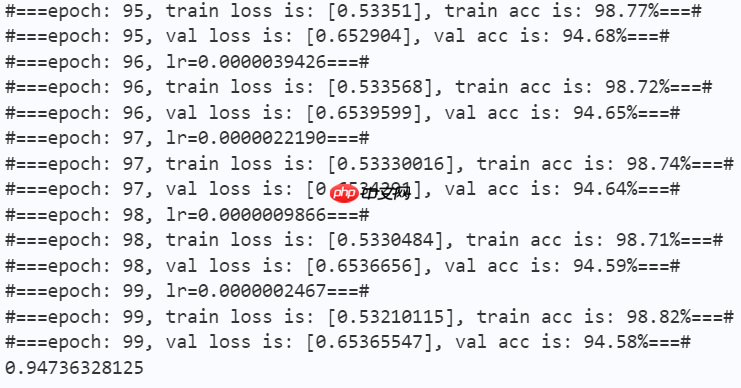
def plot_learning_curve(record, title='loss', ylabel='CE Loss'):
''' Plot learning curve of your CNN '''
maxtrain = max(map(float, record['train'][title]))
maxval = max(map(float, record['val'][title]))
ymax = max(maxtrain, maxval) * 1.1
mintrain = min(map(float, record['train'][title]))
minval = min(map(float, record['val'][title]))
ymin = min(mintrain, minval) * 0.9
total_steps = len(record['train'][title])
x_1 = list(map(int, record['train']['iter']))
x_2 = list(map(int, record['val']['iter']))
figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(x_1, record['train'][title], c='tab:red', label='train')
plt.plot(x_2, record['val'][title], c='tab:cyan', label='val')
plt.ylim(ymin, ymax)
plt.xlabel('Training steps')
plt.ylabel(ylabel)
plt.title('Learning curve of {}'.format(title))
plt.legend()
plt.show()plot_learning_curve(loss_record, title='loss', ylabel='CE Loss')
<Figure size 1000x600 with 1 Axes>
plot_learning_curve(acc_record, title='acc', ylabel='Accuracy')
<Figure size 1000x600 with 1 Axes>
import time
work_path = 'work/model'model = mobilevig_ti()
model_state_dict = paddle.load(os.path.join(work_path, 'best_model.pdparams'))
model.set_state_dict(model_state_dict)
model.eval()
aa = time.time()for batch_id, data in enumerate(val_loader):
x_data, y_data = data
labels = paddle.unsqueeze(y_data, axis=1) with paddle.no_grad():
logits = model(x_data)
bb = time.time()print("Throughout:{}".format(int(len(val_dataset)//(bb - aa))))Throughout:932
def get_cifar10_labels(labels):
"""返回CIFAR10数据集的文本标签。"""
text_labels = [ 'airplane', 'automobile', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck'] return [text_labels[int(i)] for i in labels]def show_images(imgs, num_rows, num_cols, pred=None, gt=None, scale=1.5):
"""Plot a list of images."""
figsize = (num_cols * scale, num_rows * scale)
_, axes = plt.subplots(num_rows, num_cols, figsize=figsize)
axes = axes.flatten() for i, (ax, img) in enumerate(zip(axes, imgs)): if paddle.is_tensor(img):
ax.imshow(img.numpy()) else:
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False) if pred or gt:
ax.set_title("pt: " + pred[i] + "\ngt: " + gt[i]) return axeswork_path = 'work/model'X, y = next(iter(DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=18))) model = mobilevig_ti() model_state_dict = paddle.load(os.path.join(work_path, 'best_model.pdparams')) model.set_state_dict(model_state_dict) model.eval() logits = model(X) y_pred = paddle.argmax(logits, -1) X = paddle.transpose(X, [0, 2, 3, 1]) axes = show_images(X.reshape((18, 224, 224, 3)), 1, 18, pred=get_cifar10_labels(y_pred), gt=get_cifar10_labels(y)) plt.show()
Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers).
<Figure size 2700x150 with 18 Axes>
以上就是【CVPRW 2024】MobileViG:用于移动视觉应用的基于图的稀疏注意力的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号