本文介绍了图像边缘检测的原理,指出边缘是灰度剧变处,检测基于方向导数掩码卷积。实现了通用边缘检测算子EdgeOP,集成Roberts、Prewitt等多种算子,提供四种边缘强度计算方式,并通过测试函数对比效果,展示了不同算子和计算方法的检测结果。
☞☞☞AI 智能聊天, 问答助手, AI 智能搜索, 免费无限量使用 DeepSeek R1 模型☜☜☜

图像的边缘指的是灰度值发生急剧变化的位置。
在图像形成过程中,由于亮度、纹理、颜色、阴影等物理因素的不同而导致图像灰度值发生突变,从而形成边缘。
边缘是通过检查每个像素的邻域并对其灰度变化进行量化的,这种灰度变化的量化相当于微积分里连续函数中方向导数或者离散数列的差分。
传统的边缘检测大多数是通过基于方向导数掩码(梯度方向导数)求卷积的方法。
计算灰度变化的卷积算子包含Roberts算子、Prewitt算子、Sobel算子、Scharr算子、Kirsch算子、Robinson算子、Laplacian算子。
大多数边缘检测算子是基于方向差分卷积核求卷积的方法,在使用由两个或者多个卷积核组成的边缘检测算子时假设有 n 个卷积核,记 Conv1,Conv2,...,Convn,为图像分别与个卷积核做卷积的结果,通常有四种方式来衡量最后输出的边缘强度。
取对应位置绝对值的和:∑i=1n∣convi∣
取对应位置平方和的开方:∑i=1nconvi2
取对应位置绝对值的最大值:max{∣conv1∣,∣conv2∣,...,∣convi∣}
插值法:∑i=1nai∣convi∣,其中 ai>=0,且 ∑i=1nai=1
import numpy as npimport paddleimport paddle.nn as nnclass EdgeOP(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, kernel):
'''
kernel: shape(out_channels, in_channels, h, w)
'''
super(EdgeOP, self).__init__()
out_channels, in_channels, h, w = kernel.shape
self.filter = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=(h, w), padding='SAME', bias_attr=False)
self.filter.weight.set_value(kernel.astype('float32'))
@staticmethod
def postprocess(outputs, mode=0, weight=None):
'''
Input: NCHW
Output: NHW(mode==1-3) or NCHW(mode==4)
Params:
mode: switch output mode(0-4)
weight: weight when mode==3
'''
if mode==0:
results = paddle.sum(paddle.abs(outputs), axis=1) elif mode==1:
results = paddle.sqrt(paddle.sum(paddle.pow(outputs, 2), axis=1)) elif mode==2:
results = paddle.max(paddle.abs(outputs), axis=1) elif mode==3: if weight is None:
C = outputs.shape[1]
weight = paddle.to_tensor([1/C] * C, dtype='float32') else:
weight = paddle.to_tensor(weight, dtype='float32')
results = paddle.einsum('nchw, c -> nhw', paddle.abs(outputs), weight) elif mode==4:
results = paddle.abs(outputs) return paddle.clip(results, 0, 255).cast('uint8')
@paddle.no_grad()
def forward(self, images, mode=0, weight=None):
outputs = self.filter(images) return self.postprocess(outputs, mode, weight)import osimport cv2from PIL import Imagedef test_edge_det(kernel, img_path='test.jpg'):
img = cv2.imread(img_path, 0)
img_tensor = paddle.to_tensor(img, dtype='float32')[None, None, ...]
op = EdgeOP(kernel)
all_results = [] for mode in range(4):
results = op(img_tensor, mode=mode)
all_results.append(results.numpy()[0])
results = op(img_tensor, mode=4) for result in results.numpy()[0]:
all_results.append(result) return all_results, np.concatenate(all_results, 1)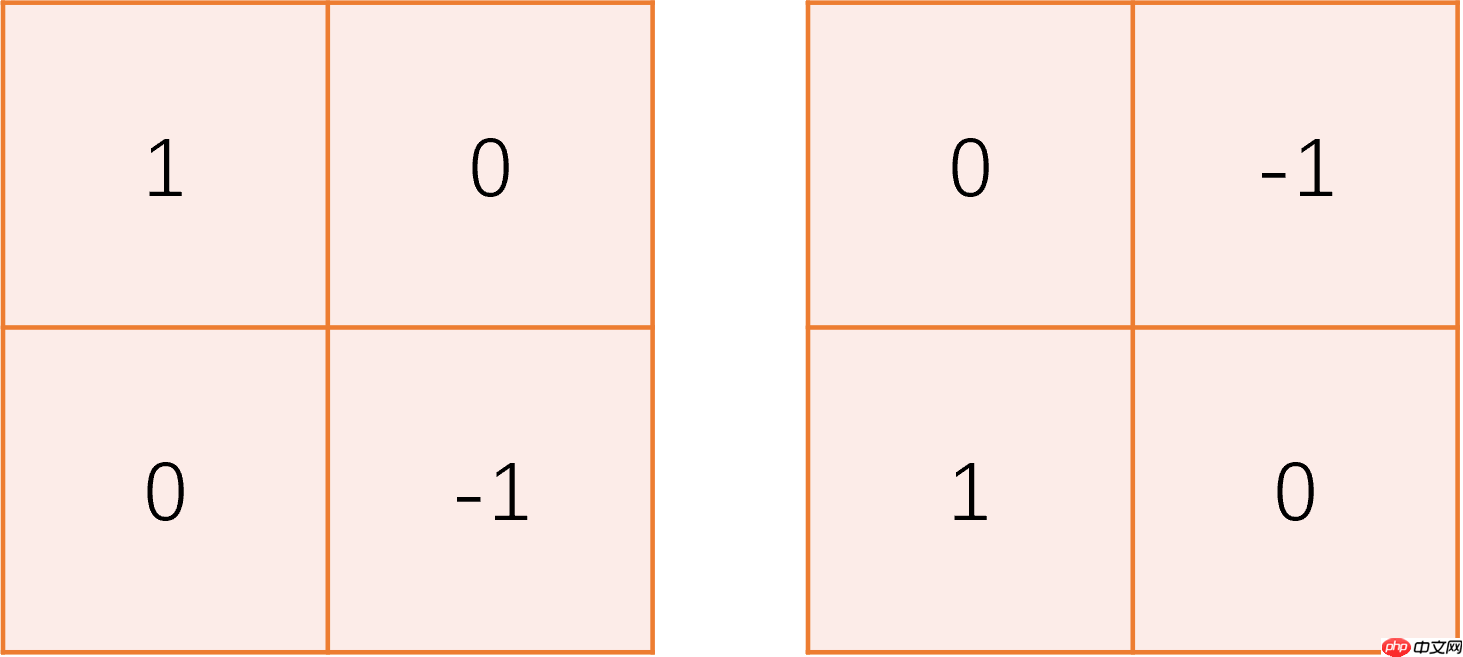
roberts_kernel = np.array([
[[
[1, 0],
[0, -1]
]],
[[
[0, -1],
[1, 0]
]]
])
_, concat_res = test_edge_det(roberts_kernel)
Image.fromarray(concat_res)<PIL.Image.Image image mode=L size=3600x600 at 0x7F2548799F10>
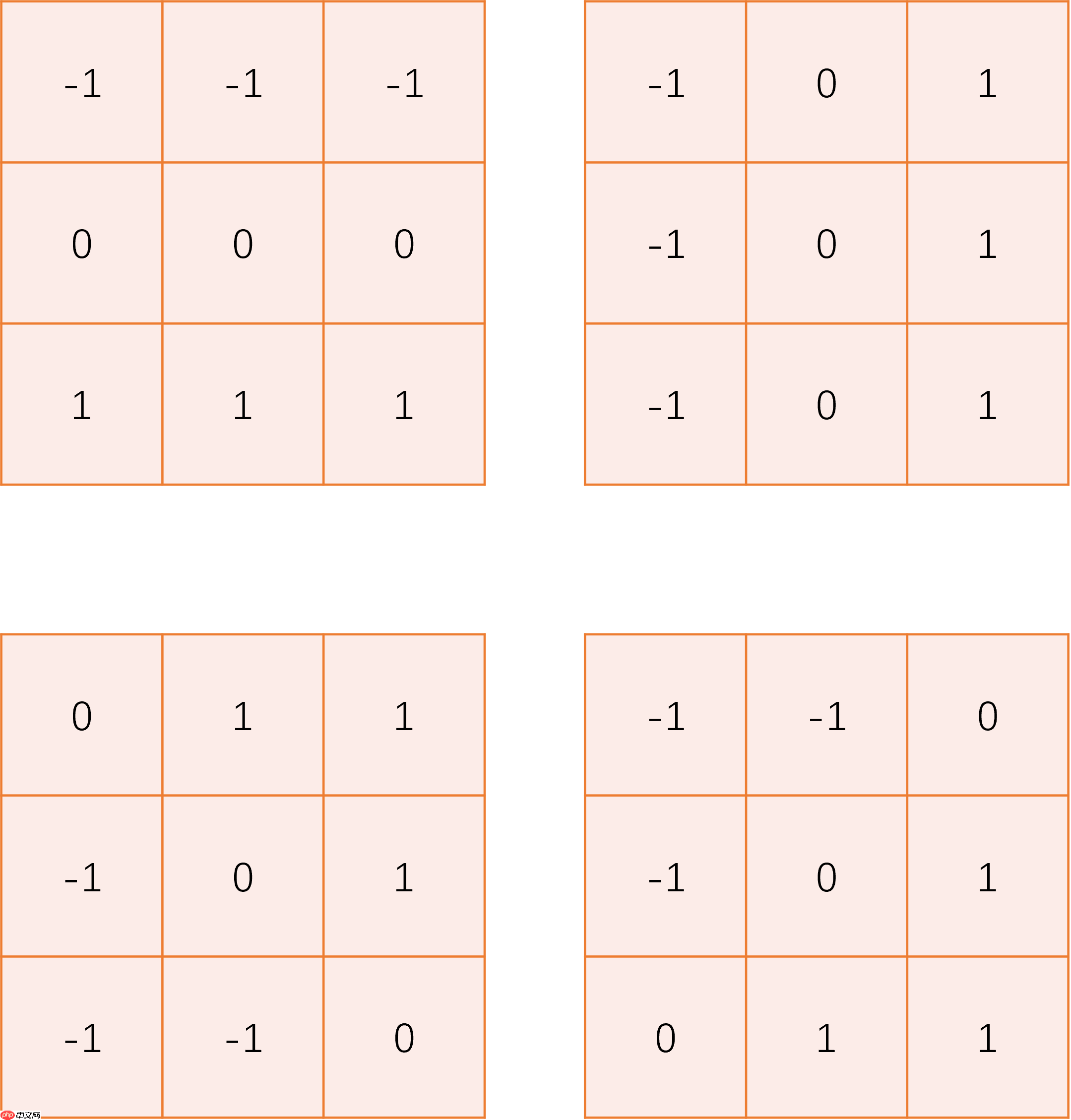
prewitt_kernel = np.array([
[[
[-1, -1, -1],
[ 0, 0, 0],
[ 1, 1, 1]
]],
[[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, 0, 1]
]],
[[
[ 0, 1, 1],
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 0]
]],
[[
[ -1, -1, 0],
[ -1, 0, 1],
[ 0, 1, 1]
]]
])
_, concat_res = test_edge_det(prewitt_kernel)
Image.fromarray(concat_res)<PIL.Image.Image image mode=L size=4800x600 at 0x7F251781EF10>
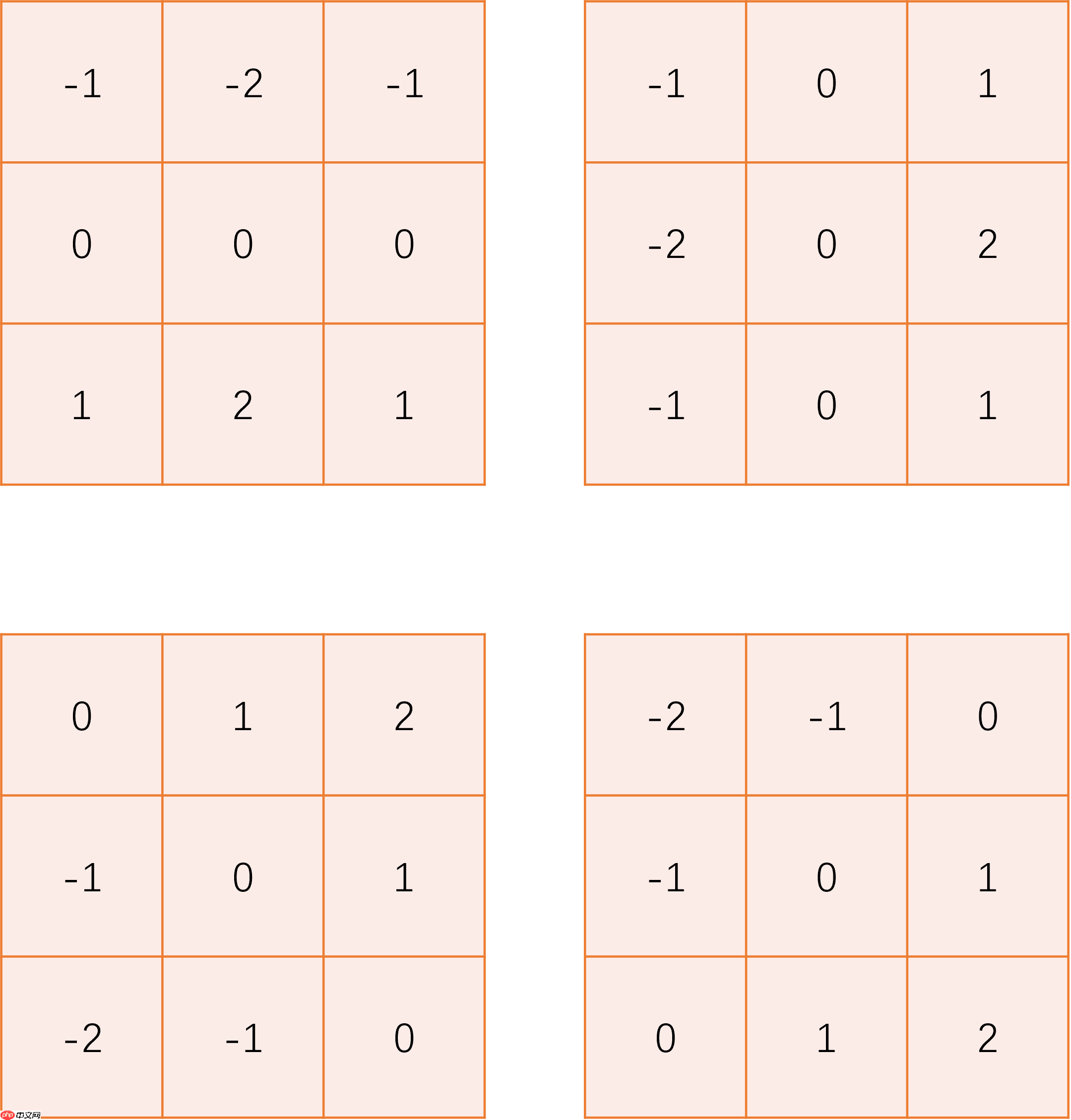
sobel_kernel = np.array([
[[
[-1, -2, -1],
[ 0, 0, 0],
[ 1, 2, 1]
]],
[[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-2, 0, 2],
[-1, 0, 1]
]],
[[
[ 0, 1, 2],
[-1, 0, 1],
[-2, -1, 0]
]],
[[
[ -2, -1, 0],
[ -1, 0, 1],
[ 0, 1, 2]
]]
])
_, concat_res = test_edge_det(sobel_kernel)
Image.fromarray(concat_res)<PIL.Image.Image image mode=L size=4800x600 at 0x7F251782E8D0>

scharr_kernel = np.array([
[[
[-3, -10, -3],
[ 0, 0, 0],
[ 3, 10, 3]
]],
[[
[-3, 0, 3],
[-10, 0, 10],
[-3, 0, 3]
]],
[[
[ 0, 3, 10],
[-3, 0, 3],
[-10, -3, 0]
]],
[[
[ -10, -3, 0],
[ -3, 0, 3],
[ 0, 3, 10]
]]
])
_, concat_res = test_edge_det(scharr_kernel)
Image.fromarray(concat_res)<PIL.Image.Image image mode=L size=4800x600 at 0x7F251782EE10>

Krisch_kernel = np.array([
[[
[5, 5, 5],
[-3,0,-3],
[-3,-3,-3]
]],
[[
[-3, 5,5],
[-3,0,5],
[-3,-3,-3]
]],
[[
[-3,-3,5],
[-3,0,5],
[-3,-3,5]
]],
[[
[-3,-3,-3],
[-3,0,5],
[-3,5,5]
]],
[[
[-3, -3, -3],
[-3,0,-3],
[5,5,5]
]],
[[
[-3, -3, -3],
[5,0,-3],
[5,5,-3]
]],
[[
[5, -3, -3],
[5,0,-3],
[5,-3,-3]
]],
[[
[5, 5, -3],
[5,0,-3],
[-3,-3,-3]
]],
])
_, concat_res = test_edge_det(Krisch_kernel)
Image.fromarray(concat_res)<PIL.Image.Image image mode=L size=7200x600 at 0x7F24FF09E4D0>
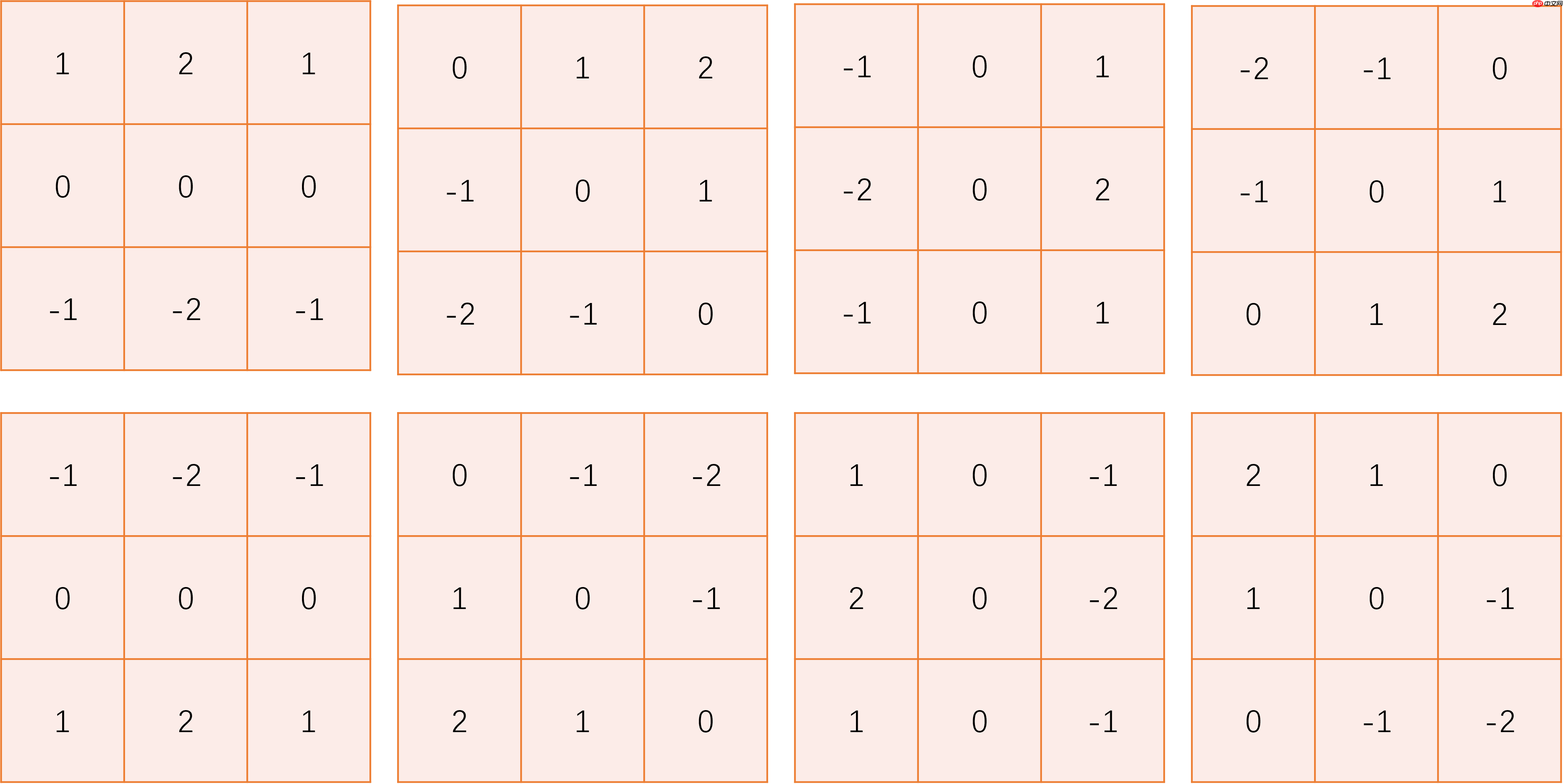
robinson_kernel = np.array([
[[
[1, 2, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[-1, -2, -1]
]],
[[
[0, 1, 2],
[-1, 0, 1],
[-2, -1, 0]
]],
[[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-2, 0, 2],
[-1, 0, 1]
]],
[[
[-2, -1, 0],
[-1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 2]
]],
[[
[-1, -2, -1],
[0, 0, 0],
[1, 2, 1]
]],
[[
[0, -1, -2],
[1, 0, -1],
[2, 1, 0]
]],
[[
[1, 0, -1],
[2, 0, -2],
[1, 0, -1]
]],
[[
[2, 1, 0],
[1, 0, -1],
[0, -1, -2]
]],
])
_, concat_res = test_edge_det(robinson_kernel)
Image.fromarray(concat_res)<PIL.Image.Image image mode=L size=7200x600 at 0x7F251782EED0>
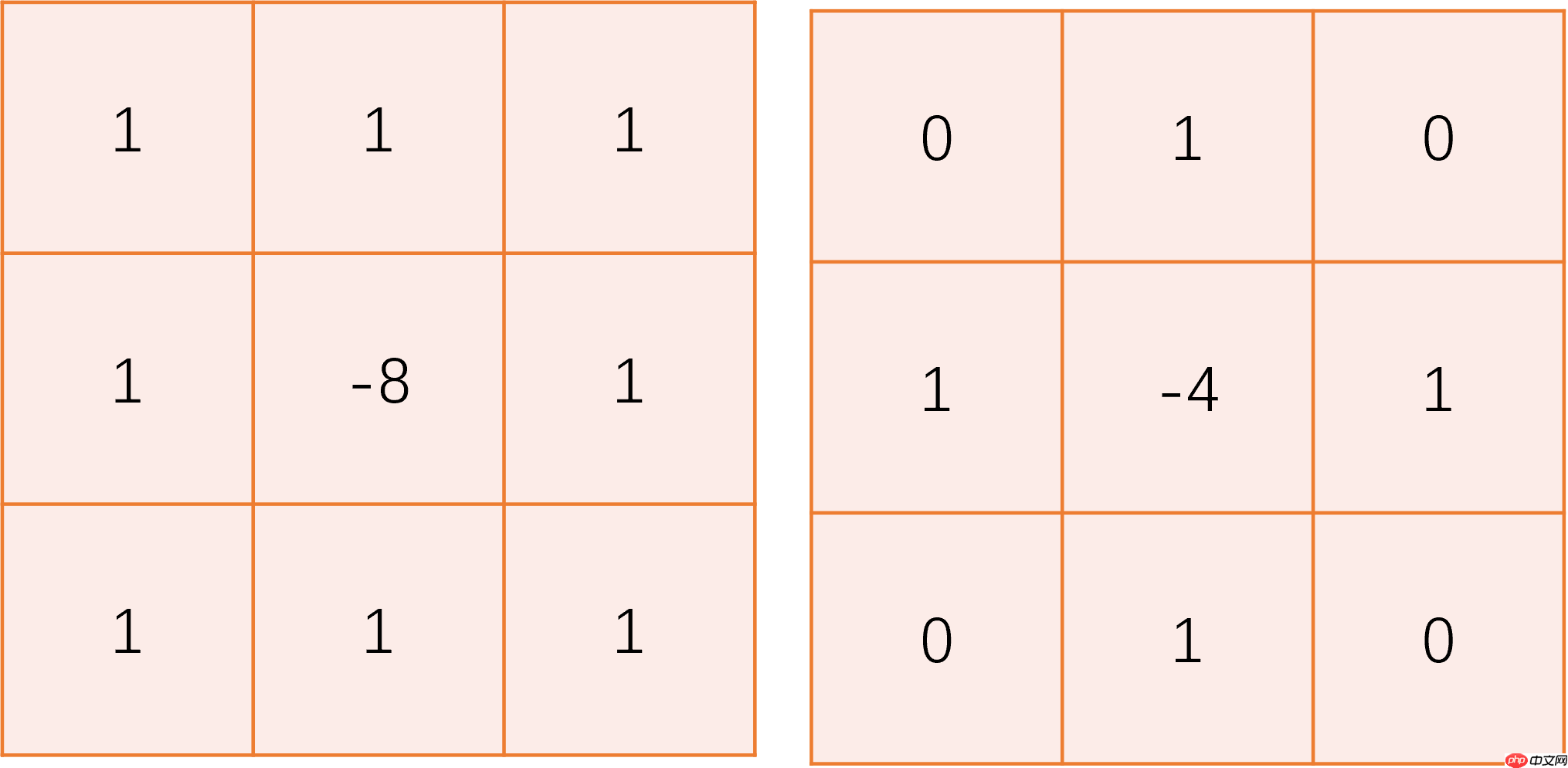
laplacian_kernel = np.array([
[[
[1, 1, 1],
[1, -8, 1],
[1, 1, 1]
]],
[[
[0, 1, 0],
[1, -4, 1],
[0, 1, 0]
]]
])
_, concat_res = test_edge_det(laplacian_kernel)
Image.fromarray(concat_res)<PIL.Image.Image image mode=L size=3600x600 at 0x7F24FF0A6A90>
以上就是边缘检测系列1:传统边缘检测算子的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号