本文介绍基于Paddle2.0实现人体姿态关键点检测的案例。先说明关键点检测的意义与两类方法,强调人体姿态检测的特殊性及常用热力图回归法。接着讲解环境设置、COCO数据集处理、数据集定义与抽样展示,还构建了基于ResNet的PoseNet模型,阐述训练过程与预测结果,展示不同训练程度模型的效果差异。
☞☞☞AI 智能聊天, 问答助手, AI 智能搜索, 免费无限量使用 DeepSeek R1 模型☜☜☜

本示例教程当前是基于2.0-rc版本Paddle做的案例实现,未来会随着2.0的系列版本发布进行升级。
在图像处理中,关键点本质上是一种特征。它是对一个固定区域或者空间物理关系的抽象描述,描述的是一定邻域范围内的组合或上下文关系。它不仅仅是一个点信息,或代表一个位置,更代表着上下文与周围邻域的组合关系。关键点检测的目标就是通过计算机从图像中找出这些点的坐标,作为计算机视觉领域的一个基础任务,关键点的检测对于高级别任务,例如识别和分类具有至关重要的意义。
关键点检测方法总体上可以分成两个类型,一个种是用坐标回归的方式来解决,另一种是将关键点建模成热力图,通过像素分类任务,回归热力图分布得到关键点位置。这两个方法,都是一种手段或者是途径,解决的问题就是要找出这个点在图像当中的位置与关系。
人脸关键点检测是最基于坐标回归的关键点检测方法,在案例Paddle2.0案例: 人脸关键点检测简要介绍如何通过飞桨开源框架实现人脸关键点检测的训练和预测。
人体姿态关键点检测(Human Keypoint Detection)又称为人体姿态识别,旨在准确定位图像之中人体关节点的位置,是人体动作识别、人体行为分析、人机交互的前置任务。与人脸关键点检测不同,人体的躯干部位更为灵活,变化更为难以预测,基于坐标回归的方法难以胜任,通常使用热力图回归的关键点检测方法。
这个案例基于人体姿态估计与追踪之关键点检测,使用新版的paddle2.0的API对人体姿态关键点模型Simple Baselines for Human Pose Estimation and Tracking进行复现,并使用集成式的训练接口,更方便地对模型进行训练和预测。
导入必要的模块,确认自己的飞桨版本。 如果是cpu环境,请安装cpu版本的paddle2.0环境,在 paddle.set_device() 输入对应运行设备。
!unzip -o cocoapi.zip -d work
!cd work/cocoapi/PythonAPI && python setup.py installprint('API安装完成')安装完成后重启环境。
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pandas as pdimport osimport argparseimport paddlefrom paddle.io import Datasetfrom paddle.vision.transforms import transformsfrom paddle.vision.models import resnet18from paddle.nn import functional as Fprint(paddle.__version__)# 选择CPU/GPU环境# device = paddle.set_device('cpu')device = paddle.set_device('gpu')from pycocotools.coco import COCOimport pdbimport randomimport cv2from work.transforms import fliplr_jointsfrom work.transforms import get_affine_transformfrom work.transforms import affine_transform2.0.0-rc1
目前COCO keypoint track是人体关键点检测的权威公开比赛之一,COCO数据集中把人体关键点表示为17个关节,分别是鼻子,左右眼,左右耳,左右肩,左右肘,左右腕,左右臀,左右膝,左右脚踝。而人体关键点检测的任务就是从输入的图片中检测到人体及对应的关键点位置。
本案例提供了两个数据集
第一个是完整的coco数据集,包含了用于多种任务的完整标注。本示例由于展示需要,第二个数据集仅从coco数据集中抽取出了100张包含人体图像,仅包含人体关键点的标注。
如果需要训练自己的数据集可以参照coco数据集格式,将自己的数据集转化为coco数据集的格式,然后使用COCOPose来读取。
其中数据集中包含的文件路径如下:
`-- coco `-- annotations |-- person_keypoints_train2017.json |-- person_keypoints_val2017.json `-- images |-- train2017 |-- val2017 |-- test2017
# 解压示例数据集!unzip -o data/data9663/coco.zip -d data/data9663/
# 或者,解压完整coco数据集!cd data/data7122 && mkdir coco !unzip -o data/data7122/train2017.zip -d data/data7122/coco/images !unzip -o data/data7122/val2017.zip -d data/data7122/coco/images !unzip -o data/data7122/annotations_trainval2017.zip -d data/data7122/coco/
飞桨(PaddlePaddle)数据集加载方案是统一使用Dataset(数据集定义) + DataLoader(多进程数据集加载)。
首先我们先进行数据集的定义,数据集定义主要是实现一个新的Dataset类,继承父类paddle.io.Dataset,并实现父类中以下两个抽象方法,getitem__和__len:
class COCOPose(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_dir, mode='train', val_split=0.1, shuffle=False, debug=False):
class config:
# 17个关键点
NUM_JOINTS = 17
# 左右对称的关键点序号
FLIP_PAIRS = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8], [9, 10], [11, 12], [13, 14], [15, 16]]
SCALE_FACTOR = 0.3
ROT_FACTOR = 40
FLIP = True
SIGMA = 3
# 裁剪patch大小
IMAGE_SIZE = [288, 384] # heatmap大小
HEATMAP_SIZE = [72, 96]
ASPECT_RATIO = IMAGE_SIZE[0] * 1.0 / IMAGE_SIZE[1]
MEAN = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
STD = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
PIXEL_STD = 200
self.cfg = config
self.cfg.DATAROOT = data_dir
self.cfg.DEBUG = debug
self.mode = mode # 划分训练集和验证集合
if self.mode in ['train', 'val']:
file_name = os.path.join(data_dir, 'annotations', 'person_keypoints_' + self.mode + '2017.json') else: raise ValueError("The dataset '{}' is not supported".format(self.mode)) # 用cocotools提供的API读取标注的json文件
coco = COCO(file_name) # Deal with class names
cats = [cat['name'] for cat in coco.loadCats(coco.getCatIds())]
classes = ['__background__'] + cats print('=> classes: {}'.format(classes))
num_classes = len(classes)
_class_to_ind = dict(zip(classes, range(num_classes)))
_class_to_coco_ind = dict(zip(cats, coco.getCatIds()))
_coco_ind_to_class_ind = dict([(_class_to_coco_ind[cls],
_class_to_ind[cls]) for cls in classes[1:]]) # Load image file names
image_set_index = coco.getImgIds()
data_len = len(image_set_index) if shuffle:
random_seed = 34
random.seed(random_seed)
random.shuffle(image_set_index)
num_images = len(image_set_index) print('=> num_images: {}'.format(num_images))
gt_db = self._load_coco_keypoint_annotation(
image_set_index, coco, _coco_ind_to_class_ind)
self.gt_db = self._select_data(gt_db) # 每次迭代时返回数据和对应的标签
def __getitem__(self, idx):
sample = self.gt_db[idx]
image_file = sample['image']
filename = sample['filename'] if 'filename' in sample else ''
joints = sample['joints_3d']
joints_vis = sample['joints_3d_vis']
c = sample['center']
s = sample['scale']
score = sample['score'] if 'score' in sample else 1
r = 0
# 读取图片
data_numpy = cv2.imread(
image_file, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR | cv2.IMREAD_IGNORE_ORIENTATION)
# 数据增广
if self.mode == 'train':
sf = self.cfg.SCALE_FACTOR
rf = self.cfg.ROT_FACTOR # 随机裁剪
s = s * np.clip(np.random.randn() * sf + 1, 1 - sf, 1 + sf)
r = np.clip(np.random.randn() * rf, -rf * 2, rf * 2) \ if random.random() <= 0.6 else 0
# 随机交换左右对称关键点坐标
if self.cfg.FLIP and random.random() <= 0.5:
data_numpy = data_numpy[:, ::-1, :]
joints, joints_vis = fliplr_joints(
joints, joints_vis, data_numpy.shape[1], self.cfg.FLIP_PAIRS)
c[0] = data_numpy.shape[1] - c[0] - 1
trans = get_affine_transform(c, s, r, self.cfg.IMAGE_SIZE)
input_img = cv2.warpAffine(
data_numpy,
trans,
(int(self.cfg.IMAGE_SIZE[0]), int(self.cfg.IMAGE_SIZE[1])),
flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) for i in range(self.cfg.NUM_JOINTS): if joints_vis[i, 0] > 0.0:
joints[i, 0:2] = affine_transform(joints[i, 0:2], trans) # 生成多通道heatmap
target, target_weight = self.generate_target(joints, joints_vis)
# 检查生成的图像
if self.cfg.DEBUG:
self.visualize(filename, data_numpy, input_img.copy(), joints, target) # 归一化(减均值、除方差)
input_img = input_img.astype('float32').transpose((2, 0, 1)) / 255
input_img -= np.array(self.cfg.MEAN).reshape((3, 1, 1))
input_img /= np.array(self.cfg.STD).reshape((3, 1, 1)) if self.mode=='train' or self.mode=='val': return input_img, target, target_weight else: return input_img, target, target_weight, c, s, score, image_file # 返回整个数据集的总数
def __len__(self):
return len(self.gt_db) # 以下函数是用来辅助读取数据
# 读取具体标注
def _load_coco_keypoint_annotation(self, image_set_index, coco, _coco_ind_to_class_ind):
"""Ground truth bbox and keypoints.
"""
print('generating coco gt_db...')
gt_db = [] for index in image_set_index:
im_ann = coco.loadImgs(index)[0]
width = im_ann['width']
height = im_ann['height']
annIds = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=index, iscrowd=False)
objs = coco.loadAnns(annIds) # Sanitize bboxes
valid_objs = [] for obj in objs:
x, y, w, h = obj['bbox']
x1 = np.max((0, x))
y1 = np.max((0, y))
x2 = np.min((width - 1, x1 + np.max((0, w - 1))))
y2 = np.min((height - 1, y1 + np.max((0, h - 1)))) if obj['area'] > 0 and x2 >= x1 and y2 >= y1:
obj['clean_bbox'] = [x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1]
valid_objs.append(obj)
objs = valid_objs
rec = [] for obj in objs:
cls = _coco_ind_to_class_ind[obj['category_id']] if cls != 1: continue
joints_3d = np.zeros((self.cfg.NUM_JOINTS, 3), dtype=np.float)
joints_3d_vis = np.zeros((self.cfg.NUM_JOINTS, 3), dtype=np.float) if self.mode in ['train', 'val']: # Ignore objs without keypoints annotation
if max(obj['keypoints']) == 0: continue
for ipt in range(self.cfg.NUM_JOINTS):
joints_3d[ipt, 0] = obj['keypoints'][ipt * 3 + 0]
joints_3d[ipt, 1] = obj['keypoints'][ipt * 3 + 1]
joints_3d[ipt, 2] = 0
t_vis = obj['keypoints'][ipt * 3 + 2] if t_vis > 1:
t_vis = 1
joints_3d_vis[ipt, 0] = t_vis
joints_3d_vis[ipt, 1] = t_vis
joints_3d_vis[ipt, 2] = 0
center, scale = self._box2cs(obj['clean_bbox'][:4])
rec.append({ 'image': os.path.join(self.cfg.DATAROOT, 'images', self.mode + '2017', '%012d.jpg' % index), 'center': center, 'scale': scale, 'joints_3d': joints_3d, 'joints_3d_vis': joints_3d_vis, 'filename': '%012d.jpg' % index, 'imgnum': 0,
})
gt_db.extend(rec) return gt_db def _select_data(self, db):
db_selected = [] for rec in db:
num_vis = 0
joints_x = 0.0
joints_y = 0.0
for joint, joint_vis in zip(
rec['joints_3d'], rec['joints_3d_vis']): if joint_vis[0] <= 0: continue
num_vis += 1
joints_x += joint[0]
joints_y += joint[1] if num_vis == 0: continue
joints_x, joints_y = joints_x / num_vis, joints_y / num_vis
area = rec['scale'][0] * rec['scale'][1] * (self.cfg.PIXEL_STD ** 2)
joints_center = np.array([joints_x, joints_y])
bbox_center = np.array(rec['center'])
diff_norm2 = np.linalg.norm((joints_center - bbox_center), 2)
ks = np.exp(-1.0 * (diff_norm2 ** 2) / ((0.2) ** 2 * 2.0 * area))
metric = (0.2 / 16) * num_vis + 0.45 - 0.2 / 16
if ks > metric:
db_selected.append(rec) print('=> num db: {}'.format(len(db))) print('=> num selected db: {}'.format(len(db_selected))) return db_selected def _box2cs(self, box):
x, y, w, h = box[:4] return self._xywh2cs(x, y, w, h) def _xywh2cs(self, x, y, w, h):
center = np.zeros((2), dtype=np.float32)
center[0] = x + w * 0.5
center[1] = y + h * 0.5
if w > self.cfg.ASPECT_RATIO * h:
h = w * 1.0 / self.cfg.ASPECT_RATIO elif w < self.cfg.ASPECT_RATIO * h:
w = h * self.cfg.ASPECT_RATIO
scale = np.array(
[w * 1.0 / self.cfg.PIXEL_STD, h * 1.0 / self.cfg.PIXEL_STD],
dtype=np.float32) if center[0] != -1:
scale = scale * 1.25
return center, scale
# 根据关键点坐标,生成热力图
def generate_target(self, joints, joints_vis):
"""
:param joints: [num_joints, 3]
:param joints_vis: [num_joints, 3]
:return: target, target_weight(1: visible, 0: invisible)
"""
NUM_JOINTS = self.cfg.NUM_JOINTS
HEATMAP_SIZE = self.cfg.HEATMAP_SIZE
IMAGE_SIZE = self.cfg.IMAGE_SIZE
SIGMA = self.cfg.SIGMA
target_weight = np.ones((NUM_JOINTS, 1), dtype=np.float32)
target_weight[:, 0] = joints_vis[:, 0]
target = np.zeros((NUM_JOINTS,
HEATMAP_SIZE[1],
HEATMAP_SIZE[0]),
dtype=np.float32)
tmp_size = SIGMA * 3
for joint_id in range(NUM_JOINTS):
feat_stride = np.array(IMAGE_SIZE) / np.array(HEATMAP_SIZE)
mu_x = int(joints[joint_id][0] / feat_stride[0] + 0.5)
mu_y = int(joints[joint_id][1] / feat_stride[1] + 0.5) # Check that any part of the gaussian is in-bounds
ul = [int(mu_x - tmp_size), int(mu_y - tmp_size)]
br = [int(mu_x + tmp_size + 1), int(mu_y + tmp_size + 1)] if ul[0] >= HEATMAP_SIZE[0] or ul[1] >= HEATMAP_SIZE[1] \ or br[0] < 0 or br[1] < 0: # If not, just return the image as is
target_weight[joint_id] = 0
continue
# Generate gaussian
size = 2 * tmp_size + 1
x = np.arange(0, size, 1, np.float32)
y = x[:, np.newaxis]
x0 = y0 = size // 2
# The gaussian is not normalized, we want the center value to equal 1
g = np.exp(- ((x - x0) ** 2 + (y - y0) ** 2) / (2 * SIGMA ** 2)) # Usable gaussian range
g_x = max(0, -ul[0]), min(br[0], HEATMAP_SIZE[0]) - ul[0]
g_y = max(0, -ul[1]), min(br[1], HEATMAP_SIZE[1]) - ul[1] # Image range
img_x = max(0, ul[0]), min(br[0], HEATMAP_SIZE[0])
img_y = max(0, ul[1]), min(br[1], HEATMAP_SIZE[1])
v = target_weight[joint_id] if v > 0.5:
target[joint_id][img_y[0]:img_y[1], img_x[0]:img_x[1]] = \
g[g_y[0]:g_y[1], g_x[0]:g_x[1]] return target, target_weight # 数据可视化
def visualize(self, filename, data_numpy, input, joints, target):
"""
:param cfg: global configurations for dataset
:param filename: the name of image file
:param data_numpy: original numpy image data
:param input: input tensor [b, c, h, w]
:param joints: [num_joints, 3]
:param target: target tensor [b, c, h, w]
"""
NUM_JOINTS = self.cfg.NUM_JOINTS from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 7))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(data_numpy, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(input, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.scatter(joints[:, 0], joints[:, 1], marker='x', s=10, color='cyan')
plt.show()
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 13)) for i in range(NUM_JOINTS):
plt.subplot(5,4,i+1)
plt.imshow(target[i])
plt.show()实现好Dataset数据集后,我们来测试一下数据集是否符合预期。在COCOPose中预留了用于数据可视化的接口visualize,只需要在数据集定义中加入flagdebug=True,迭代数据集的时候会将图像和热力图打印出来。
debug_data = COCOPose('data/data9663/coco', mode='train', shuffle=True, debug=True)
img, heatmaps, heatmaps_weight = debug_data[0]# 返回的数据分别是包含人物的patch,对应的热力图和是否包含人体关键点的去权重loading annotations into memory... Done (t=0.02s) creating index... index created! => classes: ['__background__', 'person'] => num_images: 500 generating coco gt_db... => num db: 430 => num selected db: 416
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/cbook/__init__.py:2349: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working if isinstance(obj, collections.Iterator): /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/cbook/__init__.py:2366: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working return list(data) if isinstance(data, collections.MappingView) else data
<Figure size 1080x504 with 2 Axes>
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/numpy/lib/type_check.py:546: DeprecationWarning: np.asscalar(a) is deprecated since NumPy v1.16, use a.item() instead 'a.item() instead', DeprecationWarning, stacklevel=1)
<Figure size 1080x936 with 17 Axes>
这个案例使用到的Simple Baselines模型如下图所示。
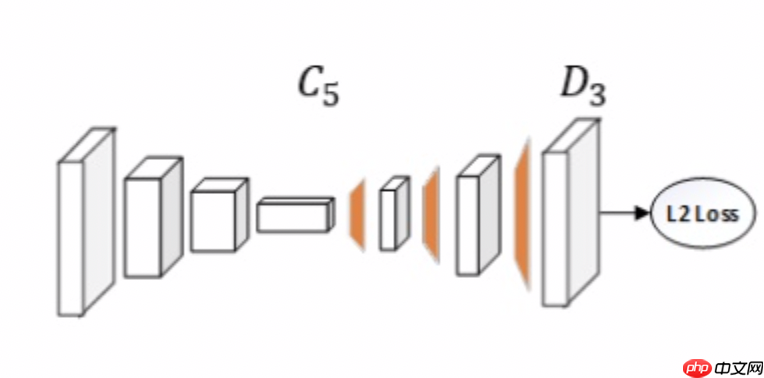
Simple Baselines模型与常用与人体关键点检测的hourglass,cpn等相比,该模型的网络结构看起来很直观简洁。网络结构就是在ResNet后加上几层Deconvolution直接生成热力图。相比于其他模型,就是使用Deconvolution替换了上采样结构。
在案例人体姿态估计与追踪之关键点检测中,网络中完整定义了ResNet。
在这个案例中,我们尝试利用Paddle2.0提供的预定义paddle.vision.models.resnet和预训练模型,来构建我们的Simple Baselines模型。
# Paddle2.0 提供的resnet50模型如下from paddle.vision.models.resnet import resnet50 res_net = resnet50()for prefix, layer in res_net.named_children(): print(prefix, layer)
conv1 <paddle.nn.layer.conv.Conv2D object at 0x7f205e525950> bn1 <paddle.nn.layer.norm.BatchNorm2D object at 0x7f205e525830> relu <paddle.nn.layer.activation.ReLU object at 0x7f205e525d70> maxpool <paddle.nn.layer.pooling.MaxPool2D object at 0x7f205e525e30> layer1 <paddle.fluid.dygraph.container.Sequential object at 0x7f205dbd3a70> layer2 <paddle.fluid.dygraph.container.Sequential object at 0x7f205dc22110> layer3 <paddle.fluid.dygraph.container.Sequential object at 0x7f205e4e18f0> layer4 <paddle.fluid.dygraph.container.Sequential object at 0x7f205dc546b0> avgpool <paddle.nn.layer.pooling.AdaptiveAvgPool2D object at 0x7f205dc54710> fc <paddle.nn.layer.common.Linear object at 0x7f205dc547d0>
ResNet在ImageNet分类任务中,图像分成1000类,所以在模型后接一个全连接层,预测出1000中类别各自的概率。我们只需要ResNet最后平均池化层avgpool和全连接层fc去掉,就得到了Simple Baselines模型的backbone部分。
下面我们定义Simple Baselines模型为PoseNet。
class PoseNet(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, layers=101, kps_num=16, pretrained=False, test_mode=False):
super(PoseNet, self).__init__()
self.k = kps_num
self.layers = layers
self.pretrained = pretrained
self.test_mode = test_mode
supported_layers = [50, 101, 152] assert layers in supported_layers, \ "supported layers are {} but input layer is {}".format(supported_layers, layers) if layers == 50: from paddle.vision.models.resnet import resnet50 as resnet elif layers == 101: from paddle.vision.models.resnet import resnet101 as resnet elif layers == 152: from paddle.vision.models.resnet import resnet152 as resnet
backbone = resnet(pretrained)
# backbone模型是去掉最末为池化和全连接层的ResNet模型
self.backbone = paddle.nn.Sequential(*(list(backbone.children())[:-2])) # 加入生成热力图部分网络,包含3层反卷积和1层1*1卷积网络
BN_MOMENTUM = 0.9
self.upLayers = paddle.nn.Sequential(
paddle.nn.Conv2DTranspose(
in_channels=2048,
out_channels=256,
kernel_size=4,
padding=1,
stride=2,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.001)),
bias_attr=False),
paddle.nn.BatchNorm2D(num_features=256, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
paddle.nn.ReLU(),
paddle.nn.Conv2DTranspose(
in_channels=256,
out_channels=256,
kernel_size=4,
padding=1,
stride=2,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.001)),
bias_attr=False),
paddle.nn.BatchNorm2D(num_features=256, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
paddle.nn.ReLU(),
paddle.nn.Conv2DTranspose(
in_channels=256,
out_channels=256,
kernel_size=4,
padding=1,
stride=2,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.001)),
bias_attr=False),
paddle.nn.BatchNorm2D(num_features=256, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
paddle.nn.ReLU(),
paddle.nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=256,
out_channels=self.k,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0, # bias_attr=False,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.001)))
) def forward(self, input,):
conv = self.backbone(input)
out = self.upLayers(conv) return out调用飞桨提供的summary接口对组建好的模型进行可视化,方便进行模型结构和参数信息的查看和确认。
输入图像为长宽为288、384的彩色图像,输出17个通道长宽为72、96的热力图。
from paddle.static import InputSpec paddle.disable_static() kp_dim = 17model = paddle.Model(PoseNet(layers=50, kps_num=kp_dim, test_mode=False))# IMAGE_SIZE = [288, 384]# HEATMAP_SIZE = [72, 96]model.summary((1, 3, 288, 384))
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Input Shape Output Shape Param #
==============================================================================
Conv2D-1 [[1, 3, 288, 384]] [1, 64, 144, 192] 9,408
BatchNorm2D-1 [[1, 64, 144, 192]] [1, 64, 144, 192] 256
ReLU-1 [[1, 64, 144, 192]] [1, 64, 144, 192] 0
MaxPool2D-1 [[1, 64, 144, 192]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 0
Conv2D-3 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 4,096
BatchNorm2D-3 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 256
ReLU-2 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 0
Conv2D-4 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 36,864
BatchNorm2D-4 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 256
Conv2D-5 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 16,384
BatchNorm2D-5 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 1,024
Conv2D-2 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 16,384
BatchNorm2D-2 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 1,024
BottleneckBlock-1 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 0
Conv2D-6 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 16,384
BatchNorm2D-6 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 256
ReLU-3 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 0
Conv2D-7 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 36,864
BatchNorm2D-7 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 256
Conv2D-8 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 16,384
BatchNorm2D-8 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 1,024
BottleneckBlock-2 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 0
Conv2D-9 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 16,384
BatchNorm2D-9 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 256
ReLU-4 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 0
Conv2D-10 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 36,864
BatchNorm2D-10 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 64, 72, 96] 256
Conv2D-11 [[1, 64, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 16,384
BatchNorm2D-11 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 1,024
BottleneckBlock-3 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 0
Conv2D-13 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 128, 72, 96] 32,768
BatchNorm2D-13 [[1, 128, 72, 96]] [1, 128, 72, 96] 512
ReLU-5 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 0
Conv2D-14 [[1, 128, 72, 96]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 147,456
BatchNorm2D-14 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 512
Conv2D-15 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 65,536
BatchNorm2D-15 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 2,048
Conv2D-12 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 131,072
BatchNorm2D-12 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 2,048
BottleneckBlock-4 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 0
Conv2D-16 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 65,536
BatchNorm2D-16 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 512
ReLU-6 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 0
Conv2D-17 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 147,456
BatchNorm2D-17 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 512
Conv2D-18 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 65,536
BatchNorm2D-18 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 2,048
BottleneckBlock-5 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 0
Conv2D-19 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 65,536
BatchNorm2D-19 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 512
ReLU-7 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 0
Conv2D-20 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 147,456
BatchNorm2D-20 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 512
Conv2D-21 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 65,536
BatchNorm2D-21 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 2,048
BottleneckBlock-6 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 0
Conv2D-22 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 65,536
BatchNorm2D-22 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 512
ReLU-8 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 0
Conv2D-23 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 147,456
BatchNorm2D-23 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 128, 36, 48] 512
Conv2D-24 [[1, 128, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 65,536
BatchNorm2D-24 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 2,048
BottleneckBlock-7 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 512, 36, 48] 0
Conv2D-26 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 256, 36, 48] 131,072
BatchNorm2D-26 [[1, 256, 36, 48]] [1, 256, 36, 48] 1,024
ReLU-9 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-27 [[1, 256, 36, 48]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 589,824
BatchNorm2D-27 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
Conv2D-28 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 262,144
BatchNorm2D-28 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 4,096
Conv2D-25 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 524,288
BatchNorm2D-25 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 4,096
BottleneckBlock-8 [[1, 512, 36, 48]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-29 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 262,144
BatchNorm2D-29 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
ReLU-10 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-30 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 589,824
BatchNorm2D-30 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
Conv2D-31 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 262,144
BatchNorm2D-31 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 4,096
BottleneckBlock-9 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-32 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 262,144
BatchNorm2D-32 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
ReLU-11 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-33 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 589,824
BatchNorm2D-33 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
Conv2D-34 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 262,144
BatchNorm2D-34 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 4,096
BottleneckBlock-10 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-35 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 262,144
BatchNorm2D-35 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
ReLU-12 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-36 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 589,824
BatchNorm2D-36 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
Conv2D-37 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 262,144
BatchNorm2D-37 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 4,096
BottleneckBlock-11 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-38 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 262,144
BatchNorm2D-38 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
ReLU-13 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-39 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 589,824
BatchNorm2D-39 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
Conv2D-40 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 262,144
BatchNorm2D-40 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 4,096
BottleneckBlock-12 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-41 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 262,144
BatchNorm2D-41 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
ReLU-14 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-42 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 589,824
BatchNorm2D-42 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
Conv2D-43 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 262,144
BatchNorm2D-43 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 4,096
BottleneckBlock-13 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 1024, 18, 24] 0
Conv2D-45 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 512, 18, 24] 524,288
BatchNorm2D-45 [[1, 512, 18, 24]] [1, 512, 18, 24] 2,048
ReLU-15 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 0
Conv2D-46 [[1, 512, 18, 24]] [1, 512, 9, 12] 2,359,296
BatchNorm2D-46 [[1, 512, 9, 12]] [1, 512, 9, 12] 2,048
Conv2D-47 [[1, 512, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 1,048,576
BatchNorm2D-47 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 8,192
Conv2D-44 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 2,097,152
BatchNorm2D-44 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 8,192
BottleneckBlock-14 [[1, 1024, 18, 24]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 0
Conv2D-48 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 512, 9, 12] 1,048,576
BatchNorm2D-48 [[1, 512, 9, 12]] [1, 512, 9, 12] 2,048
ReLU-16 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 0
Conv2D-49 [[1, 512, 9, 12]] [1, 512, 9, 12] 2,359,296
BatchNorm2D-49 [[1, 512, 9, 12]] [1, 512, 9, 12] 2,048
Conv2D-50 [[1, 512, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 1,048,576
BatchNorm2D-50 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 8,192
BottleneckBlock-15 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 0
Conv2D-51 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 512, 9, 12] 1,048,576
BatchNorm2D-51 [[1, 512, 9, 12]] [1, 512, 9, 12] 2,048
ReLU-17 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 0
Conv2D-52 [[1, 512, 9, 12]] [1, 512, 9, 12] 2,359,296
BatchNorm2D-52 [[1, 512, 9, 12]] [1, 512, 9, 12] 2,048
Conv2D-53 [[1, 512, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 1,048,576
BatchNorm2D-53 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 8,192
BottleneckBlock-16 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 2048, 9, 12] 0
Conv2DTranspose-1 [[1, 2048, 9, 12]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 8,388,608
BatchNorm2D-54 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 1,024
ReLU-18 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 18, 24] 0
Conv2DTranspose-2 [[1, 256, 18, 24]] [1, 256, 36, 48] 1,048,576
BatchNorm2D-55 [[1, 256, 36, 48]] [1, 256, 36, 48] 1,024
ReLU-19 [[1, 256, 36, 48]] [1, 256, 36, 48] 0
Conv2DTranspose-3 [[1, 256, 36, 48]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 1,048,576
BatchNorm2D-56 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 1,024
ReLU-20 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 256, 72, 96] 0
Conv2D-54 [[1, 256, 72, 96]] [1, 17, 72, 96] 4,369
==============================================================================
Total params: 34,054,353
Trainable params: 33,945,041
Non-trainable params: 109,312
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Input size (MB): 1.27
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 630.33
Params size (MB): 129.91
Estimated Total Size (MB): 761.51
------------------------------------------------------------------------------/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/paddle/distributed/parallel.py:119: UserWarning: Currently not a parallel execution environment, `paddle.distributed.init_parallel_env` will not do anything. "Currently not a parallel execution environment, `paddle.distributed.init_parallel_env` will not do anything."
{'total_params': 34054353, 'trainable_params': 33945041}在这个任务是热力图进行回归,计算每个通道生成的热力图与生成的热力图之间的差异。我们自定义HMLoss来做计算,飞桨2.0中,在nn下将损失函数封装成可调用类。我们这里使用paddle.Model相关的API直接进行训练,只需要定义好数据集、网络模型和损失函数即可。
class HMLoss(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, kps_num):
super(HMLoss, self).__init__()
self.k = kps_num def forward(self, heatmap, target, target_weight):
_, c, h, w = heatmap.shape
x = heatmap.reshape((-1, self.k, h*w))
y = target.reshape((-1, self.k, h*w))
w = target_weight.reshape((-1, self.k))
x = x.split(num_or_sections=self.k, axis=1)
y = y.split(num_or_sections=self.k, axis=1)
w = w.split(num_or_sections=self.k, axis=1)
# 计算预测热力图的目标热力图的均方误差
_list = [] for idx in range(self.k):
_tmp = paddle.scale(x=x[idx] - y[idx], scale=1.)
_tmp = _tmp * _tmp
_tmp = paddle.mean(_tmp, axis=2)
_list.append(_tmp * w[idx])
_loss = paddle.concat(_list, axis=0)
_loss = paddle.mean(_loss) return 0.5 * _loss使用模型代码进行Model实例生成,使用prepare接口定义优化器、损失函数和评价指标等信息,用于后续训练使用。在所有初步配置完成后,调用fit接口开启训练执行过程,调用fit时只需要将前面定义好的训练数据集、测试数据集、训练轮次(Epoch)和批次大小(batch_size)配置好即可。
# 定义训练用的超参数parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=__doc__)
parser.add_argument('--batch_size', type=int, default=128, help="Minibatch size totally.")
parser.add_argument('--num_epochs', type=int, default=140, help="Number of epochs.")
parser.add_argument('--model_save_dir', type=str, default="checkpoint", help="Model save directory")# pretrained:使用paddle2.0提供的ImageNet预训练的ResNet模型parser.add_argument('--pretrained', type=bool, default=True, help="Whether to use pretrained ResNet model.")
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.001, help="Set learning rate.")
parser.add_argument('--lr_strategy', type=str, default="piecewise_decay", help="Set the learning rate decay strategy.")
args = parser.parse_args([])from visualdl import LogReader, LogWriter# 配置visualdlwrite = LogWriter(logdir='logdir')#iters 初始化为0iters = 0class Callbk(paddle.callbacks.Callback):
def __init__(self, write, iters=0):
self.write = write
self.iters = iters def on_train_batch_end(self, step, logs):
self.iters += 1
#记录loss
self.write.add_scalar(tag="loss",step=self.iters,value=logs['loss'][0]) #记录 accuracy
# self.write.add_scalar(tag="acc",step=self.iters,value=logs['acc'])
m = logs['SaveOutput'][0].sum(0).reshape([96,72,1])
self.write.add_image(tag="output Heatmaps",step=self.iters, img=(m-m.min())/(m.max()-m.min())*255)# 利用Mertic接口记录预测的Output heatmapclass SaveOutput(paddle.metric.Metric):
def __init__(self, name='SaveOutput', ):
super(SaveOutput, self).__init__()
self._name = name def update(self, preds, target, target_weight):
self.preds = preds def accumulate(self):
return self.preds def name(self):
return self._name def reset(self):
passkp_dim = 17# IMAGE_SIZE = [288, 384]# HEATMAP_SIZE = [72, 96]# 调用COCOPose定义数据集# 使用示例数据集# train_data = COCOPose('data/data9663/coco', mode='train', shuffle=True)# 使用完整COCO数据集train_data = COCOPose('data/data7122/coco', mode='train', shuffle=True)
val_data = COCOPose('data/data7122/coco', mode='val')# 定义模型net = PoseNet(layers=50, kps_num=kp_dim, pretrained=args.pretrained, test_mode=False)
model = paddle.Model(net)# 选择优化策略if args.lr_strategy=='piecewise_decay':
num_train_img = train_data.__len__()
batch_size = args.batch_size
step = int(num_train_img / batch_size + 1)
bd = [0.6, 0.85]
bd = [int(args.num_epochs * e * step) for e in bd]
lr_drop_ratio = 0.1
base_lr = args.lr
lr = [base_lr * (lr_drop_ratio**i) for i in range(len(bd) + 1)]
scheduler = paddle.optimizer.lr.PiecewiseDecay(boundaries=bd, values=lr, verbose=False)
optim = paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=scheduler,
parameters=model.parameters())else:
optim = paddle.optimizer.Momentum(learning_rate=args.lr,
momentum=0.9,
weight_decay=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.0005))# 准备模型的优化策略和损失函数,用自定义的Metric来保存图像model.prepare(optimizer=optim, loss=HMLoss(kps_num=kp_dim), metrics=SaveOutput())# 使用示例数据集进行10个epoch训练# model.fit(train_data, batch_size=args.batch_size, epochs=100, callbacks=Callbk(write=write, iters=iters))# 使用完整COCO数据集训练model.fit(train_data, val_data, batch_size=args.batch_size, epochs=args.num_epochs, eval_freq=1,
log_freq=1, save_dir=args.model_save_dir, save_freq=5, shuffle=True, num_workers=0,
callbacks=Callbk(write=write, iters=iters))
model.save('checkpoint/test', training=True) # save for trainingmodel.save('inference_model', training=False) # save for inference启动VisualDL,我们可以看到LogWritter记录下了训练过程中损失函数的变化曲线。这是在完整COCO数据集上训练一个epoch的曲线变化。
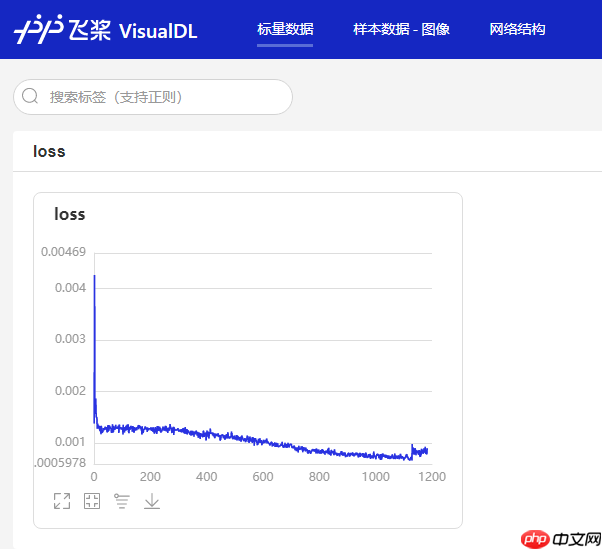
可以在样本数据-图像标签页中看到存储的图像数据,这里保存了每个batch第一个样本输出热力图多通道之和,可以看到训练完一个epoch后,热力图收敛的趋势已经比较明显。
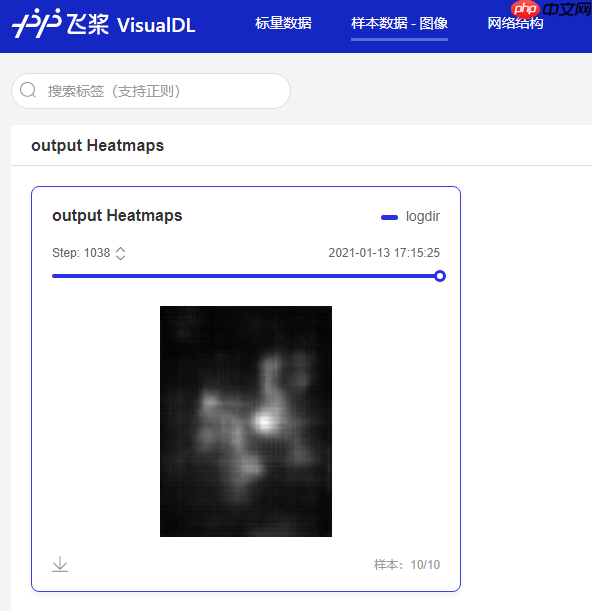
由于训练完整COCO数据集140个epoch需要花费较多的时间和算力,这里提供几个训练好的模型来进行对test文件夹中测试图片进行预测,体验不同训练程度的预测效果。
注:由于练完整COCO数据集没有包含类被标签,对于没有人物的图像做预测没有意义。
# 这里定义一个用于读取test文件夹的数据读取接口class COCOPose_test(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_dir,):
class config:
# 裁剪patch大小
IMAGE_SIZE = [288, 384] # heatmap大小
ASPECT_RATIO = IMAGE_SIZE[0] * 1.0 / IMAGE_SIZE[1]
MEAN = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
STD = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
self.cfg = config
self.cfg.DATAROOT = data_dir
self.file_list = os.listdir(data_dir) def __getitem__(self, idx):
filename = self.file_list[idx]
image_file = os.path.join(self.cfg.DATAROOT, filename)
file_id = int(filename.split('.')[0]) input = cv2.imread(
image_file, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR | cv2.IMREAD_IGNORE_ORIENTATION) input = cv2.resize(input, (int(self.cfg.IMAGE_SIZE[0]), int(self.cfg.IMAGE_SIZE[1]))) # Normalization
input = input.astype('float32').transpose((2, 0, 1)) / 255
input -= np.array(self.cfg.MEAN).reshape((3, 1, 1)) input /= np.array(self.cfg.STD).reshape((3, 1, 1)) return input, file_id
def __len__(self):
return len(self.file_list)
test_data = COCOPose_test(data_dir='test')net = PoseNet(layers=50, kps_num=17, pretrained=False, test_mode=False)
net_pd = paddle.load('output/0.pdparams')
net.set_state_dict(net_pd)
model = paddle.Model(net)
model.prepare()
result = model.predict(test_data, batch_size=1)Predict begin... step 6/6 [==============================] - 34ms/step Predict samples: 6
查看预测结果的
id = 2image, img_id = test_data[id]
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(image.transpose(1,2,0), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 13))for i in range(17):
plt.subplot(5,4,i+1)
plt.imshow(result[0][id][0][i])Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers).
<Figure size 432x288 with 1 Axes>
<Figure size 1080x936 with 17 Axes>
基于旧版Paddle完成的复现paddle,提供了静态图下的完整COCO预训练模型pose-resnet50-coco-384x288.zip。
!tar xf pose-resnet50-coco-384x288.tar.gz -C pretrained
旧版的Paddle静态图模型与新版的命名规则不一样,需要将文件名进行映射。
net = PoseNet(layers=50, kps_num=17, pretrained=False, test_mode=False)
net_sd = net.state_dict()# 读取旧版的模型load_layer_state_dict = paddle.load('pretrained/pose-resnet50-coco-384x288')
pretrain_sd = sorted(list(load_layer_state_dict.keys()))model_sd = sorted(list(net_sd.keys()))
j = 0for i in range(len(pretrain_sd)): # print(i)
if 'bias' in model_sd[i]: if j <= 55:
name_bias = 'batch_norm_'+str(j)+'.b_0'
print(model_sd[i], net_sd[model_sd[i]].shape , load_layer_state_dict[name_bias].shape,)
net_sd[model_sd[i]] = \
paddle.to_tensor(load_layer_state_dict[name_bias], \
place=net_sd[model_sd[i]].place,\
stop_gradient=net_sd[model_sd[i]].stop_gradient) else: print('??.b_0', model_sd[i], net_sd[model_sd[i]].shape )
net_sd['upLayers.9.bias'] = \
paddle.to_tensor(load_layer_state_dict['conv2d_53.b_0'], \
place=net_sd[model_sd[i]].place,\
stop_gradient=net_sd[model_sd[i]].stop_gradient) if '_mean' in model_sd[i]: if j <= 55:
name_mean = 'batch_norm_'+str(j)+'.w_1'
print(model_sd[i], net_sd[model_sd[i]].shape , load_layer_state_dict[name_mean].shape,)
net_sd[model_sd[i]] = \
paddle.to_tensor(load_layer_state_dict[name_mean], \
place=net_sd[model_sd[i]].place,\
stop_gradient=net_sd[model_sd[i]].stop_gradient)
else: print('??.w_1', model_sd[i], net_sd[model_sd[i]].shape ) if '_variance' in model_sd[i]: if j <= 55:
name_variance = 'batch_norm_'+str(j)+'.w_2'
print(model_sd[i], net_sd[model_sd[i]].shape , load_layer_state_dict[name_variance].shape,)
net_sd[model_sd[i]] = \
paddle.to_tensor(load_layer_state_dict[name_variance], \
place=net_sd[model_sd[i]].place,\
stop_gradient=net_sd[model_sd[i]].stop_gradient)
else: print('??.w_2', model_sd[i], net_sd[model_sd[i]].shape ) # j += 1
if ('backbone.1' in model_sd[i] or 'downsample.1' in model_sd[i] or\ 'upLayers.1' in model_sd[i] or 'upLayers.4' in model_sd[i] or \ 'upLayers.7' in model_sd[i] or 'upLayers.9' in model_sd[i] or 'bn' in model_sd[i])\ and 'weight' in model_sd[i]: if j <= 55:
name_weight = 'batch_norm_'+str(j)+'.w_0'
print(model_sd[i], net_sd[model_sd[i]].shape , load_layer_state_dict[name_weight].shape,)
net_sd[model_sd[i]] = \
paddle.to_tensor(load_layer_state_dict[name_weight], \
place=net_sd[model_sd[i]].place,\
stop_gradient=net_sd[model_sd[i]].stop_gradient)
else: print('??.w_0', model_sd[i], net_sd[model_sd[i]].shape ) print(j)
j += 1
j = 0name_list = [n for n in net_sd.keys() if len(net_sd[n].shape)>1]for i in range(len(name_list)):
name = name_list[i] if len(net_sd[name].shape)>1: if j<53:
name_layer = 'conv2d_'+str(j)+'.w_0'
print(i, j, name, net_sd[name].shape) print(i, j, name_layer, load_layer_state_dict[name_layer].shape)
net_sd[name] = \
paddle.to_tensor(load_layer_state_dict[name_layer], \
place=net_sd[name].place,\
stop_gradient=net_sd[name].stop_gradient)
elif 53<=j<56:
name_layer = 'conv2d_transpose_'+str(j-53)+'.w_0'
print(i, j, name, net_sd[name].shape) print(i, j, name_layer, load_layer_state_dict[name_layer].shape)
net_sd[name] = \
paddle.to_tensor(load_layer_state_dict[name_layer], \
place=net_sd[name].place,\
stop_gradient=net_sd[name].stop_gradient)
elif j==56:
name_layer = 'conv2d_53.w_0'
print(i, j, name, net_sd[name].shape) print(i, j, name_layer, load_layer_state_dict[name_layer].shape)
net_sd[name] = \
paddle.to_tensor(load_layer_state_dict[name_layer], \
place=net_sd[name].place,\
stop_gradient=net_sd[name].stop_gradient)
j+=1# 加载模型net.set_state_dict(net_sd)
# 进行预测model = paddle.Model(net) model.prepare() result = model.predict(test_data, batch_size=1)
Predict begin... step 6/6 [==============================] - 41ms/step Predict samples: 6
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/paddle/distributed/parallel.py:119: UserWarning: Currently not a parallel execution environment, `paddle.distributed.init_parallel_env` will not do anything. "Currently not a parallel execution environment, `paddle.distributed.init_parallel_env` will not do anything."
# 改变id查看输出的结果id = 2image, img_id = test_data[id]
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(image.transpose(1,2,0), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 13))for i in range(17):
plt.subplot(5,4,i+1)
plt.imshow(result[0][id][0][i])Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/numpy/lib/type_check.py:546: DeprecationWarning: np.asscalar(a) is deprecated since NumPy v1.16, use a.item() instead 'a.item() instead', DeprecationWarning, stacklevel=1)
<Figure size 432x288 with 1 Axes>
<Figure size 1080x936 with 17 Axes>
通过对比两个实验结果可以看到,使用ImageNet预训练、经过一个完整的COCO训练集一个epoch的模型已经开始收敛,热力图已经汇聚成点的形状。 而使用官方提供的训练好的模型,性能提升更为明显。
以上就是Paddle2.0案例: 人体姿态关键点检测的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号