这周的学习内容承接上周的文章!
在上次文章的结尾,我们提到了使用Statement接口时可能会面临SQL注入的风险,不建议大家使用。为了解决SQL注入问题,我们转而使用PreparedStatement接口(详细内容请参阅上一篇文章:第27次文章:简单了解JDBC)。
下面我们直接提供测试代码:
import com.mysql.jdbc.Connection;
/**
* 测试PreparedStatement的基本用法
*/
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
//加载驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
conn = (Connection) DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testjdbc", "root", "123456");
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false;"> String sql = "insert into t_user1 (username,pwd,regTime) value (?,?,?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// ps.setString(1, "peng");
// ps.setString(2, "123456");
// ps.setDate(3, new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));//获取当前时间
System.out.println("插入一条语句");
ps.setObject(1, "peng");
ps.setObject(2, "123456");
ps.setObject(3, new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));//获取当前时间
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(ps != null) {
ps.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}} }
注意事项:
当我们从Statement接口转向PreparedStatement接口后,参数不再通过拼接字符串的方式传递,而是在SQL命令中使用“?”作为占位符。这正是PreparedStatement防止SQL注入的关键所在。如我们在注释掉的代码段中所示,使用PreparedStatement对象ps的setString、setDate等方法向每个占位符传递参数。这样可以预先判断参数是否符合String、int等类型,从而避免了向SQL语句中注入恶意指令的情况。
在向SQL语句中输入参数时,我们不仅可以使用setXXX方法,还可以直接使用setObject()方法传递参数,此时无需考虑不同参数类型的区别,全部作为Object类型传递。
使用setDate()方法时,需要使用数据库中的时间类型java.sql.Date,注意这与Java中的Date类型不同。
(5)Result接口
Statement执行SQL语句返回Result结果集。
Result提供了检索不同类型字段的方法,常用的包括:
getString():获取数据库中类型为varchar、char等的对象 getFloat():获取数据库中类型为Float的对象 getDate():获取数据库中类型为Date的对象 getBoolean():获取数据库中类型为Boolean的对象
测试Result接口:
import com.mysql.jdbc.Connection;
/** </p><ul><li><p>测试ResultSet结果集的基本用法
*/
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//加载驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
conn = (Connection) DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testjdbc", "root", "123456");
String sql = "select id,username,pwd from t_user where id>?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setObject(1, 1);//取出所有id大于等于2的记录
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)+"---"+rs.getString(2)+"---"+rs.getInt(3));//一次取出第1列,第2列,第3列
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(ps != null) {
ps.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}注意事项:
在此代码中,我们仍然使用PreparedStatement类型来传递参数,使用“?”作为占位符,向占位符中传递我们需要大于的参数值。
使用Result接口时,可以将其视为一个容器,用于接收返回的id大于2的结果。然后通过编写一个while循环来输出结果集中的内容。其中,rs.next()方法类似于迭代器中的hasNext()方法。
(6)依序关闭使用的对象及连接
Result——>Statement——>Connection
(7)批处理
Batch
对于大量的批处理操作,建议使用Statement,因为PreparedStatement的预编译空间有限,当数据量特别大时,可能会发生异常。
测试批处理操作:
import com.mysql.jdbc.Connection;
/** </p></li><li><p>测试批处理的基本用法
*/
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//加载驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
conn = (Connection) DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testjdbc", "root", "123456");
conn.setAutoCommit(false); //设为手动提交
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
stmt = conn.createStatement();</p><p>for (int i=0;i<100000;i++) {
stmt.addBatch("insert into t_user1 (username,pwd,regTime) values ('user"+i+"','pwd"+i+"',now())");
}
stmt.executeBatch();
conn.commit();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("批处理执行时间:"+(end-start)+"ms");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
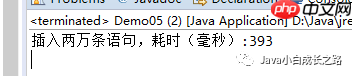
}
注意事项:
在进行批处理时,需要注意两点:第一,将PreparedStatement接口替换为Statement接口;第二,将连接的事务提交设为手动提交。
以上就是第28次文章:简单了解JDBC(续上周)的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号