OGNL:对象视图导航语言. ${user.addr.name} 这种写法就叫对象视图导航。
OGNL不仅仅可以视图导航.支持比EL表达式更加丰富的功能。
struts2 的包中已经包含了.所以不需要导入额外的jar包

立即学习“Java免费学习笔记(深入)”;
@Test//准备工作public void fun1() throws Exception{//准备OGNLContext//准备RootUser rootUser = new User("tom",18);//准备ContextMap<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();//将rootUser作为root部分 oc.setRoot(rootUser);//将context这个Map作为Context部分 oc.setValues(context);//书写OGNLOgnl.getValue("", oc, oc.getRoot());
}
//取出root中user对象的name属性String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("age", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
//取出context中键为user1对象的name属性String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user2.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#user2.age", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
System.out.println(age);
//将root中的user对象的name属性赋值Ognl.getValue("name='jerry'", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name='郝强勇',#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
//调用root中user对象的setName方法Ognl.getValue("setName('lilei')", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("getName()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.setName('lucy'),#user1.getName()", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("@cn.itheima.a_ognl.HahaUtils@echo('hello 强勇!')", oc, oc.getRoot());//Double pi = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.Math@PI", oc, oc.getRoot());Double pi = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@@PI", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(pi);
//创建list对象Integer size = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}[0]", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.get(1)", oc, oc.getRoot()); /*System.out.println(size);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);*///创建Map对象Integer size2 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name3 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}['name']", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.get('age')", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(size2);
System.out.println(name3);
System.out.println(age);

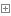
ValueStack中的两部分


栈是由ArrayList模拟的

栈中的两个方法的实现

访问栈中属性的特点.由上到下

默认情况下,栈中放置当前访问的Action对象



Context部分就是ActionContext数据中心


如何获得值栈对象,值栈对象与ActionContext对象是互相引用的
//压入栈顶//1获得值栈ValueStack vs = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();//2将u压入栈顶vs.push(u);
<action name="Demo3Action" class="cn.itheima.d_config.Demo3Action" method="execute" ><result name="success" type="redirectAction" ><param name="actionName">Demo1Action</param><param name="namespace">/</param><!-- 如果添加的参数struts"看不懂".就会作为参数附加重定向的路径之后.
如果参数是动态的.可以使用${}包裹ognl表达式.动态取值 --><param name="name">${name}</param></result></action>查找顺序:

public String list() throws Exception {//1 接受参数String cust_name = ServletActionContext.getRequest().getParameter("cust_name");//2 创建离线查询对象DetachedCriteria dc =DetachedCriteria.forClass(Customer.class);//3 判断参数拼装条件if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(cust_name)){
dc.add(Restrictions.like("cust_name", "%"+cust_name+"%"));
}//4 调用Service将离线对象传递List<Customer> list = cs.getAll(dc);//5 将返回的list放入request域.转发到list.jsp显示 //ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("list", list);// 放到ActionContextActionContext.getContext().put("list", list); return "list";
}
<s:iterator value="#list" var="cust" >
<TR
style="FONT-WEIGHT: normal; FONT-STYLE: normal; BACKGROUND-COLOR: white; TEXT-DECORATION: none">
<TD>
<s:property value="#cust.cust_name" />
</TD>
<TD>
<s:property value="#cust.cust_level" />
</TD>
<TD>
<s:property value="#cust.cust_source" />
</TD>
<TD>
<s:property value="#cust.cust_linkman" />
</TD>
<TD>
<s:property value="#cust.cust_phone" />
</TD>
<TD>
<s:property value="#cust.cust_mobile" />
</TD>
<TD>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/customerServlet?method=edit&custId=${customer.cust_id}">修改</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/customerServlet?method=delete&custId=${customer.cust_id}">删除</a>
</TD>
</TR>
</s:iterator>
<%-- <s:iterator value="#list" >
<TR
style="FONT-WEIGHT: normal; FONT-STYLE: normal; BACKGROUND-COLOR: white; TEXT-DECORATION: none">
<TD>
<s:property value="cust_name" />
</TD>
<TD>
<s:property value="cust_level" />
</TD>
<TD>
<s:property value="cust_source" />
</TD>
<TD>
<s:property value="cust_linkman" />
</TD>
<TD>
<s:property value="cust_phone" />
</TD>
<TD>
<s:property value="cust_mobile" />
</TD>
<TD>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/customerServlet?method=edit&custId=${customer.cust_id}">修改</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/customerServlet?method=delete&custId=${customer.cust_id}">删除</a>
</TD>
</TR>
</s:iterator> --%>注意:<s:iterator value="#list" var="cust" > 每次都会把cust存在ActionContext中
以上就是JAVA之:OGNL表达式练习的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

java怎么学习?java怎么入门?java在哪学?java怎么学才快?不用担心,这里为大家提供了java速学教程(入门到精通),有需要的小伙伴保存下载就能学习啦!

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号