☞☞☞AI 智能聊天, 问答助手, AI 智能搜索, 免费无限量使用 DeepSeek R1 模型☜☜☜

在使用c++进行CUDA算子开发
在GPU上面运行tanh算子,可以看到官方实现的算子和我们自己实现的CUDA算子的前向输出和回传梯度都一致 安装自己实现的tanh算子,运行后请刷新下环境!!!
!python setup.py install
import numpy as np
x = np.random.random((4, 10)).astype("float32")print(x)[[0.8485352 0.82548 0.6914224 0.33665353 0.5060949 0.12096553 0.93415546 0.66898936 0.36616254 0.61785257] [0.9686086 0.8368737 0.87306726 0.5306038 0.35964754 0.09533529 0.6159888 0.5113984 0.3554379 0.92584795] [0.5851171 0.87855285 0.8729009 0.16328739 0.06106287 0.03119349 0.6431769 0.46255094 0.39092144 0.6841152 ] [0.41889587 0.85792965 0.48324853 0.8920178 0.7228439 0.2088154 0.18290831 0.74242246 0.770023 0.89185 ]]
import paddle
paddle_x = paddle.to_tensor(x, place=paddle.CUDAPlace(0))
paddle_x.stop_gradient = Falsepaddle_y = paddle.tanh(paddle_x)
paddle_y.backward()
grad = paddle_x.gradient()print("==========================================================")print("前向传播:")print(paddle_y)print("==========================================================")print("检测是否在GPU上:")print(paddle_y.place)print("==========================================================")print("梯度:")print(grad)W0112 18:06:20.751464 7652 device_context.cc:447] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 7.0, Driver API Version: 10.1, Runtime API Version: 10.1 W0112 18:06:20.756742 7652 device_context.cc:465] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 7.6.
==========================================================
前向传播:
Tensor(shape=[4, 10], dtype=float32, place=CUDAPlace(0), stop_gradient=False,
[[0.69030344, 0.67804146, 0.59889495, 0.32448652, 0.46689692, 0.12037896,
0.73252547, 0.58431470, 0.35063058, 0.54963106],
[0.74809217, 0.68414962, 0.70292914, 0.48584250, 0.34490353, 0.09504751,
0.54832906, 0.47103402, 0.34118930, 0.72865224],
[0.52637470, 0.70569360, 0.70284498, 0.16185147, 0.06098709, 0.03118338,
0.56705880, 0.43216103, 0.37215433, 0.59418815],
[0.39599988, 0.69518942, 0.44884148, 0.71238893, 0.61866784, 0.20583236,
0.18089549, 0.63060653, 0.64694285, 0.71230626]])
==========================================================
检测是否在GPU上:
CUDAPlace(0)
==========================================================
梯度:
[[0.52348113 0.5402598 0.6413248 0.8947085 0.7820073 0.9855089
0.46340644 0.6585763 0.8770582 0.6979057 ]
[0.4403581 0.53193927 0.5058906 0.7639571 0.8810415 0.99096596
0.6993352 0.77812696 0.88358986 0.4690659 ]
[0.72292966 0.5019965 0.5060089 0.9738041 0.99628055 0.9990276
0.6784443 0.81323683 0.86150116 0.6469404 ]
[0.8431841 0.51671165 0.7985413 0.492502 0.6172501 0.957633
0.9672768 0.6023354 0.58146495 0.49261978]]1、安装tanh算子,运行后请刷新下环境!!!(前面已经安装了)
!python setup.py install
2、开始测试
立即学习“C++免费学习笔记(深入)”;
import paddlefrom custom_ops import tanh_op
custom_ops_x = paddle.to_tensor(x, place=paddle.CUDAPlace(0))
custom_ops_x.stop_gradient = Falsecustom_ops_y = tanh_op(custom_ops_x)
custom_ops_y.backward()
grad = custom_ops_x.gradient()print("==========================================================")print("前向传播:")print(custom_ops_y)print("==========================================================")print("检测是否在GPU上:")print(custom_ops_y.place)print("==========================================================")print("梯度:")print(grad)==========================================================
前向传播:
Tensor(shape=[4, 10], dtype=float32, place=CUDAPlace(0), stop_gradient=False,
[[0.69030344, 0.67804146, 0.59889495, 0.32448652, 0.46689692, 0.12037896,
0.73252547, 0.58431470, 0.35063058, 0.54963106],
[0.74809217, 0.68414962, 0.70292914, 0.48584250, 0.34490353, 0.09504751,
0.54832906, 0.47103402, 0.34118930, 0.72865224],
[0.52637470, 0.70569360, 0.70284498, 0.16185147, 0.06098709, 0.03118338,
0.56705880, 0.43216103, 0.37215433, 0.59418815],
[0.39599988, 0.69518942, 0.44884148, 0.71238893, 0.61866784, 0.20583236,
0.18089549, 0.63060653, 0.64694285, 0.71230626]])
==========================================================
检测是否在GPU上:
CUDAPlace(0)
==========================================================
梯度:
[[0.52348113 0.5402598 0.6413248 0.8947085 0.7820073 0.9855089
0.46340644 0.6585763 0.8770582 0.6979057 ]
[0.4403581 0.53193927 0.5058906 0.7639571 0.8810415 0.99096596
0.6993352 0.77812696 0.88358986 0.4690659 ]
[0.72292966 0.5019965 0.5060089 0.9738041 0.99628055 0.9990276
0.6784443 0.81323683 0.86150116 0.6469404 ]
[0.8431841 0.51671165 0.7985413 0.492502 0.6172501 0.957633
0.9672768 0.6023354 0.58146495 0.49261978]].cu文件主要是实现该算子的运算部分,在使用setup.py对算子进行安装时,nvcc程序针对.cu文件进行编译,并最终包含进动态链接库
1、引入头文件,以及定义一个block含有的thread数目
#include <paddle/extension.h>#include <vector>#include <cuda.h>#include <cuda_runtime.h>#define BLOCK 512
2、定义前向传播运算函数
该函数是一个CUDA特有声明为__global__的模板函数,负责具体执行运算部分
这里的blockIdx,blockDim,threadIdx分别表示block索引,block维度,thread索引,GPU上有多个并发的线程同时负责以上计算,用gid=blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x这一语句用来计算绝对索引,负责返回数据中某个位置处值,这样就只需要关注于单个线程计算过程
template<typename data_t>
__global__ void tanh_forward_cuda_kernel(const data_t* input_data,
data_t* output_data, int input_numel){ int gid = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; for(int i=gid; i<input_numel; i+=blockDim.x*gridDim.x){
output_data[i] = std::tanh(input_data[i]);
}
} 3、定义前向传播启动函数
该函数是一个返回paddle::Tensor类型的函数,负责对输入进行一些转换,数据初始化以及返回前向传播运算成果
这里的PD_DISPATCH_FLOATING_TYPES这个宏,实现了动态分发机制(dynamic dispatch),即它会在运行时,根据输入具体的数值类型,去决定之前CUDA kernel模块函数需要实例化为哪种函数吗,这也是之前用模板类data_t的原因。
PD_DISPATCH_FLOATING_TYPES这个宏函数,传入的参数有三个:数据类型,用来报错的函数名、一个Lambda函数
①数据类型可以通过.type()获取
②用来报错的函数名可以自己命名,一般与该算子作用相关
③Lambda函数部分([&]表示该Lambda表达式中用到的外部变量是传引用的)包括前面2中实现的运算函数tanh_forward_cuda_kernel;运算函数后面用到了<<< >>>这一写法启动kernel,其中需要根据输出大小分配grid数(用grid = (input_numel + BLOCK - 1) / BLOCK算出来),并设置每一block中的thread数(宏定义中的BLOCK),还有传入tensor目前所在的stream;接着就是( )里面传递参数进运算函数tanh_forward_cuda_kernel
std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_forward_cuda(const paddle::Tensor &input){
auto output = paddle::Tensor(paddle::PlaceType::kGPU, input.shape()); int input_numel = input.size(); int grid = (input_numel + BLOCK - 1) / BLOCK;
PD_DISPATCH_FLOATING_TYPES( input.type(), "tanh_forward_cuda_kernel", ([&] {
tanh_forward_cuda_kernel<data_t><<<grid, BLOCK, 0, input.stream()>>>( input.data<data_t>(),
output.mutable_data<data_t>(input.place()),
input_numel
);
})
); return {output};
} 4、同理,定义反向回传的运算函数和启动函数
template<typename data_t>
__global__ void tanh_backward_cuda_kernel(const data_t* input_data,
const data_t* output_grad_data,
data_t* input_grad_data, int output_numel){ int gid = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; for(int i=gid; i<output_numel; i+=blockDim.x*gridDim.x){
input_grad_data[i] = output_grad_data[i] * (1 - std::pow(std::tanh(input_data[i]), 2));
}
}
std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_backward_cuda(const paddle::Tensor &input,
const paddle::Tensor &output,
const paddle::Tensor &output_grad){
auto input_grad = paddle::Tensor(paddle::PlaceType::kGPU, input.shape()); int output_numel = output.size(); int grid = (output_numel + BLOCK - 1) / BLOCK;
PD_DISPATCH_FLOATING_TYPES( input.type(), "tanh_backward_cuda_kernel", ([&] {
tanh_backward_cuda_kernel<data_t><<<grid, BLOCK, 0, input.stream()>>>( input.data<data_t>(),
output_grad.data<data_t>(),
input_grad.mutable_data<data_t>(input.place()),
output_numel
);
})
); return {input_grad};
}#include <paddle/extension.h>#include <vector>#include <cuda.h>#include <cuda_runtime.h>#define BLOCK 512template<typename data_t>
__global__ void tanh_forward_cuda_kernel(const data_t* input_data,
data_t* output_data, int input_numel){ int gid = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; for(int i=gid; i<input_numel; i+=blockDim.x*gridDim.x){
output_data[i] = std::tanh(input_data[i]);
}
}
template<typename data_t>
__global__ void tanh_backward_cuda_kernel(const data_t* input_data,
const data_t* output_grad_data,
data_t* input_grad_data, int output_numel){ int gid = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; for(int i=gid; i<output_numel; i+=blockDim.x*gridDim.x){
input_grad_data[i] = output_grad_data[i] * (1 - std::pow(std::tanh(input_data[i]), 2));
}
}
std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_forward_cuda(const paddle::Tensor &input){
auto output = paddle::Tensor(paddle::PlaceType::kGPU, input.shape()); int input_numel = input.size(); int grid = (input_numel + BLOCK - 1) / BLOCK;
PD_DISPATCH_FLOATING_TYPES( input.type(), "tanh_forward_cuda_kernel", ([&] {
tanh_forward_cuda_kernel<data_t><<<grid, BLOCK, 0, input.stream()>>>( input.data<data_t>(),
output.mutable_data<data_t>(input.place()),
input_numel
);
})
); return {output};
}
std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_backward_cuda(const paddle::Tensor &input,
const paddle::Tensor &output,
const paddle::Tensor &output_grad){
auto input_grad = paddle::Tensor(paddle::PlaceType::kGPU, input.shape()); int output_numel = output.size(); int grid = (output_numel + BLOCK - 1) / BLOCK;
PD_DISPATCH_FLOATING_TYPES( input.type(), "tanh_backward_cuda_kernel", ([&] {
tanh_backward_cuda_kernel<data_t><<<grid, BLOCK, 0, input.stream()>>>( input.data<data_t>(),
output_grad.data<data_t>(),
input_grad.mutable_data<data_t>(input.place()),
output_numel
);
})
); return {input_grad};
}.cpp文件是为了使得可以在python中调用CUDA kernel函数,它调用上面.cu文件中启动函数,绑定到python中使用
1、引入头文件,以及定义PADDLE_WITH_CUDA和CHECK_INPUT(x)
①PADDLE_WITH_CUDA是用来能够获取Tensor.steam(),详细可看官方定义下的代码
#if defined(PADDLE_WITH_CUDA) /// \bref Get current stream of Tensor cudaStream_t stream() const;#elif defined(PADDLE_WITH_HIP) hipStream_t stream() const;#endif
#include <paddle/extension.h>#include <vector>#define PADDLE_WITH_CUDA#define CHECK_INPUT(x) PD_CHECK(x.place() == paddle::PlaceType::kGPU, #x " must be a GPU Tensor.")
2、声明.cu里的启动函数,以便后面编程时进行联想以及让编译器知道这么一个函数
std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_forward_cuda(const paddle::Tensor &input);
std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_backward_cuda(const paddle::Tensor &input,
const paddle::Tensor &output,
const paddle::Tensor &output_grad);3、编写前向传播函数,主要实现调用.cu里的前向传播启动函数
std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_forward(const paddle::Tensor& input) {
CHECK_INPUT(input); return tanh_forward_cuda(input);
}4、编写反向传播函数,主要实现调用.cu里的反向回传启动函数
std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_backward(const paddle::Tensor& input,
const paddle::Tensor& output,
const paddle::Tensor& output_grad) {
CHECK_INPUT(input);
CHECK_INPUT(output);
CHECK_INPUT(output_grad); return tanh_backward_cuda(input, output, output_grad);
} 5、使用PD_BUILD_OP系列宏,构建算子的描述信息,实现python与c++算子的绑定,作用有点类似PYBIND11_MODULE
PD_BUILD_OP:用于构建前向算子
PD_BUILD_GRAD_OP:用于构建前向算子对应的反向算子
注意:构建同一个算子的前向、反向实现,宏后面使用的算子名需要保持一致(此例中的tanh_op)
注意:PD_BUILD_OP与PD_BUILD_GRAD_OP中的Inputs与Outputs的name有强关联,对于前向算子的某个输入,如果反向算子仍然要复用,那么其name一定要保持一致(此例中的Inputs({"input"}和Outputs({"output"}),因为内部执行时,会以name作为key去查找对应的变量,比如这里前向算子的input与反向算子的input指代同一个Tensor
PD_BUILD_OP(tanh_op)
.Inputs({"input"})
.Outputs({"output"})
.SetKernelFn(PD_KERNEL(tanh_forward));
PD_BUILD_GRAD_OP(tanh_op)
.Inputs({"input", "output", paddle::Grad("output")})
.Outputs({paddle::Grad("input")})
.SetKernelFn(PD_KERNEL(tanh_backward));#include <paddle/extension.h>#include <vector>#define PADDLE_WITH_CUDA#define CHECK_INPUT(x) PD_CHECK(x.place() == paddle::PlaceType::kGPU, #x " must be a GPU Tensor.")std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_forward_cuda(const paddle::Tensor &input);
std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_backward_cuda(const paddle::Tensor &input,
const paddle::Tensor &output,
const paddle::Tensor &output_grad);
std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_forward(const paddle::Tensor& input) {
CHECK_INPUT(input); return tanh_forward_cuda(input);
}
std::vector<paddle::Tensor> tanh_backward(const paddle::Tensor& input,
const paddle::Tensor& output,
const paddle::Tensor& output_grad) {
CHECK_INPUT(input);
CHECK_INPUT(output);
CHECK_INPUT(output_grad); return tanh_backward_cuda(input, output, output_grad);
}
PD_BUILD_OP(tanh_op)
.Inputs({"input"})
.Outputs({"output"})
.SetKernelFn(PD_KERNEL(tanh_forward));
PD_BUILD_GRAD_OP(tanh_op)
.Inputs({"input", "output", paddle::Grad("output")})
.Outputs({paddle::Grad("input")})
.SetKernelFn(PD_KERNEL(tanh_backward)); .py文件主要是实现该算子安装
在安装后引用该算子,以此为例,是通过from custom_ops import tanh_op来引用的
其中custom_ops来自setup.py部分的name里
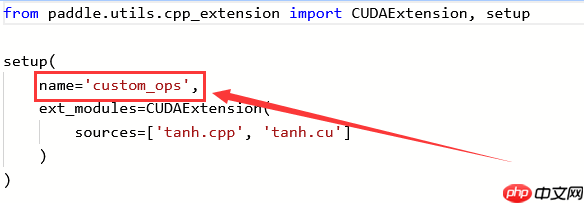
其中tan_op来自.cpp部分的PD_BUILD_OP里

from paddle.utils.cpp_extension import CUDAExtension, setup
setup(
name='custom_ops',
ext_modules=CUDAExtension(
sources=['tanh.cpp', 'tanh.cu']
)
)以上就是c++++扩展算子开发③:CUDA算子的开发的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

c++怎么学习?c++怎么入门?c++在哪学?c++怎么学才快?不用担心,这里为大家提供了c++速学教程(入门到精通),有需要的小伙伴保存下载就能学习啦!

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号