本机环境:linux 4.4.0-21-generic #37-ubuntu smp mon apr 18 18:33:37 utc 2016 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 gnu/linux
Buffer的类图如下:
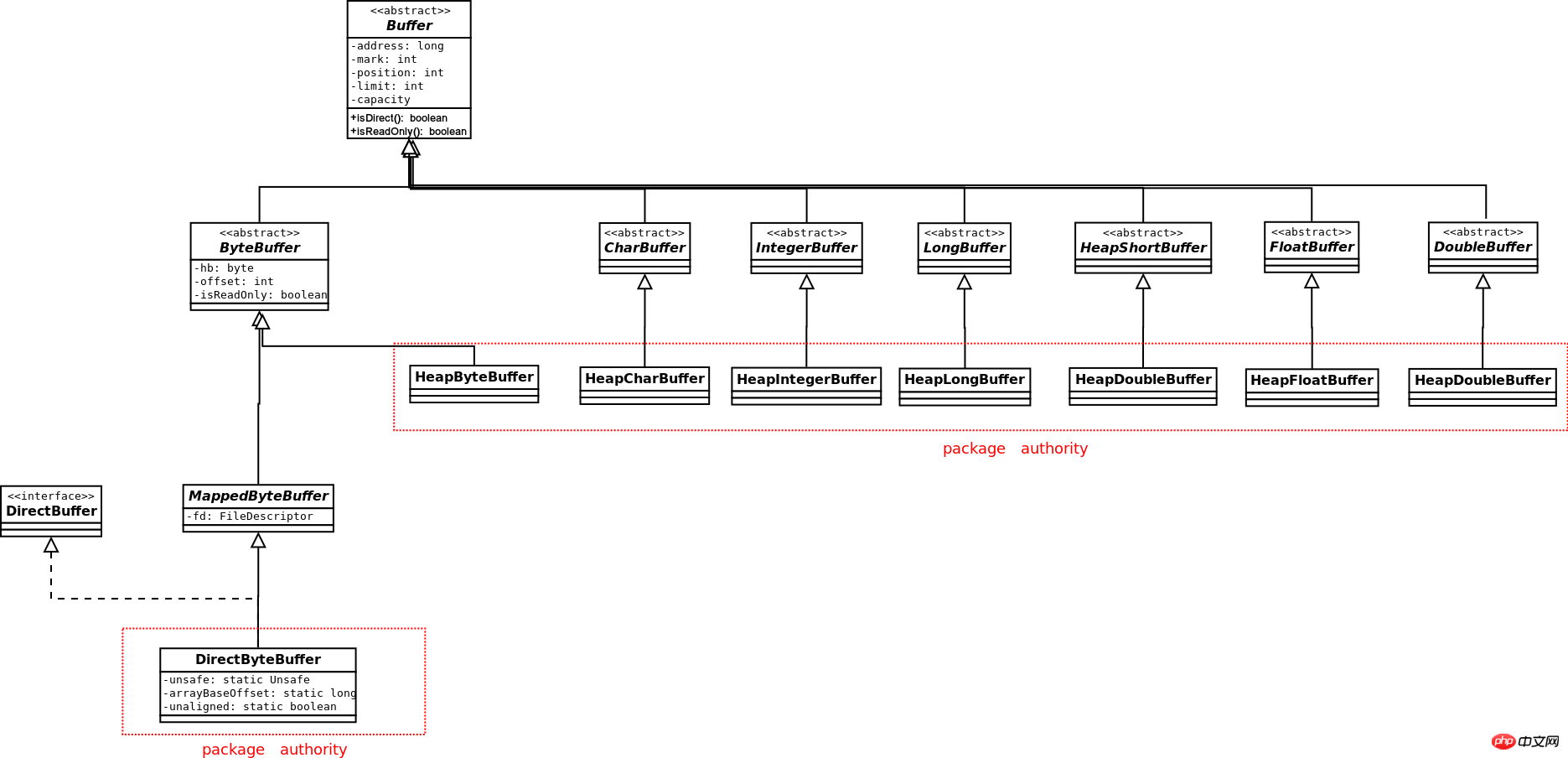
除了Boolean,其他基本数据类型都有对应的Buffer,但是只有ByteBuffer才能和Channel交互。只有ByteBuffer才能产生Direct的buffer,其他数据类型的Buffer只能产生Heap类型的Buffer。ByteBuffer可以产生其他数据类型的视图Buffer,如果ByteBuffer本身是Direct的,则产生的各视图Buffer也是Direct的。
首选说说JVM是怎么进行IO操作的。
立即学习“Java免费学习笔记(深入)”;
JVM在需要通过操作系统调用完成IO操作,比如可以通过read系统调用完成文件的读取。read的原型是:ssize_t read(int fd,void *buf,size_t nbytes),和其他的IO系统调用类似,一般需要缓冲区作为其中一个参数,该缓冲区要求是连续的。
Buffer分为Direct和Heap两类,下面分别说明这两类buffer。
Heap类型的Buffer存在于JVM的堆上,这部分内存的回收与整理和普通的对象一样。Heap类型的Buffer对象都包含一个对应基本数据类型的数组属性(比如:final **[] hb),数组才是Heap类型Buffer的底层缓冲区。
但是Heap类型的Buffer不能作为缓冲区参数直接进行系统调用,主要因为下面两个原因。
JVM在GC时可能会移动缓冲区(复制-整理),缓冲区的地址不固定。
系统调用时,缓冲区需要是连续的,但是数组可能不是连续的(JVM的实现没要求连续)。
所以使用Heap类型的Buffer进行IO时,JVM需要产生一个临时Direct类型的Buffer,然后进行数据复制,再使用临时Direct的Buffer作为参数进行操作系统调用。这造成很低的效率,主要是因为两个原因:
需要把数据从Heap类型的Buffer里面复制到临时创建的Direct的Buffer里面。
可能产生大量的Buffer对象,从而提高GC的频率。所以在IO操作时,可以通过重复利用Buffer进行优化。
Direct类型的buffer,不存在于堆上,而是JVM通过malloc直接分配的一段连续的内存,这部分内存成为直接内存,JVM进行IO系统调用时使用的是直接内存作为缓冲区。-XX:MaxDirectMemorySize,通过这个配置可以设置允许分配的最大直接内存的大小(MappedByteBuffer分配的内存不受此配置影响)。
直接内存的回收和堆内存的回收不同,如果直接内存使用不当,很容易造成OutOfMemoryError。JAVA没有提供显示的方法去主动释放直接内存,sun.misc.Unsafe类可以进行直接的底层内存操作,通过该类可以主动释放和管理直接内存。同理,也应该重复利用直接内存以提高效率。
This is a little bit backwards: By rights MappedByteBuffer should be a subclass of DirectByteBuffer, but to keep the spec clear and simple, and for optimization purposes, it's easier to do it the other way around.This works because DirectByteBuffer is a package-private class.(本段话摘自MappedByteBuffer的源码)
实际上,MappedByteBuffer属于映射buffer(自己看看虚拟内存),但是DirectByteBuffer只是说明该部分内存是JVM在直接内存区分配的连续缓冲区,并不一是映射的。也就是说MappedByteBuffer应该是DirectByteBuffer的子类,但是为了方便和优化,把MappedByteBuffer作为了DirectByteBuffer的父类。另外,虽然MappedByteBuffer在逻辑上应该是DirectByteBuffer的子类,而且MappedByteBuffer的内存的GC和直接内存的GC类似(和堆GC不同),但是分配的MappedByteBuffer的大小不受-XX:MaxDirectMemorySize参数影响。
MappedByteBuffer封装的是内存映射文件操作,也就是只能进行文件IO操作。MappedByteBuffer是根据mmap产生的映射缓冲区,这部分缓冲区被映射到对应的文件页上,属于直接内存在用户态,通过MappedByteBuffer可以直接操作映射缓冲区,而这部分缓冲区又被映射到文件页上,操作系统通过对应内存页的调入和调出完成文件的写入和写出。
通过FileChannel.map(MapMode mode,long position, long size)得到MappedByteBuffer,下面结合源码说明MappedByteBuffer的产生过程。
FileChannel.map的源码:
public MappedByteBuffer map(MapMode mode, long position, long size)throws IOException
{ensureOpen();if (position < 0L)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative position");if (size < 0L)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative size");if (position + size < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Position + size overflow");//最大2Gif (size > Integer.MAX_VALUE)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Size exceeds Integer.MAX_VALUE");int imode = -1;if (mode == MapMode.READ_ONLY)
imode = MAP_RO;else if (mode == MapMode.READ_WRITE)
imode = MAP_RW;else if (mode == MapMode.PRIVATE)
imode = MAP_PV;assert (imode >= 0);if ((mode != MapMode.READ_ONLY) && !writable)throw new NonWritableChannelException();if (!readable)throw new NonReadableChannelException();long addr = -1;int ti = -1;try {begin();
ti = threads.add();if (!isOpen())return null;//size()返回实际的文件大小//如果实际文件大小不符合,则增大文件的大小,文件的大小被改变,文件增大的部分默认设置为0。if (size() < position + size) { // Extend file sizeif (!writable) {throw new IOException("Channel not open for writing " +"- cannot extend file to required size");
}int rv;do { //增大文件的大小rv = nd.truncate(fd, position + size);
} while ((rv == IOStatus.INTERRUPTED) && isOpen());
}//如果要求映射的文件大小为0,则不调用操作系统的mmap调用,只是生成一个空间容量为0的DirectByteBuffer//并返回if (size == 0) {
addr = 0;// a valid file descriptor is not requiredFileDescriptor dummy = new FileDescriptor();if ((!writable) || (imode == MAP_RO))return Util.newMappedByteBufferR(0, 0, dummy, null);elsereturn Util.newMappedByteBuffer(0, 0, dummy, null);
}//allocationGranularity的大小在我的系统上是4K//页对齐,pagePosition为第多少页int pagePosition = (int)(position % allocationGranularity);//从页的最开始映射long mapPosition = position - pagePosition;//因为从页的最开始映射,增大映射空间long mapSize = size + pagePosition;try {// If no exception was thrown from map0, the address is valid//native方法,源代码在openjdk/jdk/src/solaris/native/sun/nio/ch/FileChannelImpl.c,//参见下面的说明addr = map0(imode, mapPosition, mapSize);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {// An OutOfMemoryError may indicate that we've exhausted memory// so force gc and re-attempt mapSystem.gc();try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException y) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}try {
addr = map0(imode, mapPosition, mapSize);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError y) {// After a second OOME, failthrow new IOException("Map failed", y);
}
}// On Windows, and potentially other platforms, we need an open// file descriptor for some mapping operations.FileDescriptor mfd;try {
mfd = nd.duplicateForMapping(fd);
} catch (IOException ioe) {unmap0(addr, mapSize);throw ioe;
}assert (IOStatus.checkAll(addr));assert (addr % allocationGranularity == 0);int isize = (int)size;
Unmapper um = new Unmapper(addr, mapSize, isize, mfd);if ((!writable) || (imode == MAP_RO)) {return Util.newMappedByteBufferR(isize,
addr + pagePosition,
mfd,
um);
} else {return Util.newMappedByteBuffer(isize,
addr + pagePosition,
mfd,
um);
}
} finally {
threads.remove(ti);end(IOStatus.checkAll(addr));
}
}map0的源码实现:
JNIEXPORT jlong JNICALL
Java_sun_nio_ch_FileChannelImpl_map0(JNIEnv *env, jobject this,
jint prot, jlong off, jlong len)
{void *mapAddress = 0;
jobject fdo = (*env)->GetObjectField(env, this, chan_fd);//linux系统调用是通过整型的文件id引用文件的,这里得到文件idjint fd = fdval(env, fdo);int protections = 0;int flags = 0;if (prot == sun_nio_ch_FileChannelImpl_MAP_RO) {
protections = PROT_READ;
flags = MAP_SHARED;
} else if (prot == sun_nio_ch_FileChannelImpl_MAP_RW) {
protections = PROT_WRITE | PROT_READ;
flags = MAP_SHARED;
} else if (prot == sun_nio_ch_FileChannelImpl_MAP_PV) {
protections = PROT_WRITE | PROT_READ;
flags = MAP_PRIVATE;
}//这里就是操作系统调用了,mmap64是宏定义,实际最后调用的是mmapmapAddress = mmap64(0, /* Let OS decide location */len, /* Number of bytes to map */protections, /* File permissions */flags, /* Changes are shared */fd, /* File descriptor of mapped file */off); /* Offset into file */if (mapAddress == MAP_FAILED) {if (errno == ENOMEM) {//如果没有映射成功,直接抛出OutOfMemoryErrorJNU_ThrowOutOfMemoryError(env, "Map failed");return IOS_THROWN;
}return handle(env, -1, "Map failed");
}return ((jlong) (unsigned long) mapAddress);
}虽然FileChannel.map()的zise参数是long,但是size的大小最大为Integer.MAX_VALUE,也就是最大只能映射最大2G大小的空间。实际上操作系统提供的MMAP可以分配更大的空间,但是JAVA限制在2G,ByteBuffer等Buffer也最大只能分配2G大小的缓冲区。
MappedByteBuffer是通过mmap产生得到的缓冲区,这部分缓冲区是由操作系统直接创建和管理的,最后JVM通过unmmap让操作系统直接释放这部分内存。
下面以ByteBuffer为例,说明Heap类型Buffer的细节。
该类型的Buffer可以通过下面方式产生:
ByteBuffer.allocate(int capacity)
ByteBuffer.wrap(byte[] array)
使用传入的数组作为底层缓冲区,变更数组会影响缓冲区,变更缓冲区也会影响数组。
ByteBuffer.wrap(byte[] array,int offset, int length)
使用传入的数组的一部分作为底层缓冲区,变更数组的对应部分会影响缓冲区,变更缓冲区也会影响数组。
DirectByteBuffer只能通过ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(int capacity) 产生。ByteBuffer.allocateDirect()源码如下:
public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity) {return new DirectByteBuffer(capacity);
}DirectByteBuffer()源码如下:
DirectByteBuffer(int cap) { // package-private
super(-1, 0, cap, cap);
//直接内存是否要页对齐,我本机测试的不用
boolean pa = VM.isDirectMemoryPageAligned();
//页的大小,本机测试的是4K
int ps = Bits.pageSize();
//如果页对齐,则size的大小是ps+cap,ps是一页,cap也是从新的一页开始,也就是页对齐了
long size = Math.max(1L, (long)cap + (pa ? ps : 0));
//JVM维护所有直接内存的大小,如果已分配的直接内存加上本次要分配的大小超过允许分配的直接内存的最大值会
//引起GC,否则允许分配并把已分配的直接内存总量加上本次分配的大小。如果GC之后,还是超过所允许的最大值,
//则throw new OutOfMemoryError("Direct buffer memory");
Bits.reserveMemory(size, cap);
long base = 0;
try {
//是吧,unsafe可以直接操作底层内存
base = unsafe.allocateMemory(size);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {、
//没有分配成功,把刚刚加上的已分配的直接内存的大小减去。
Bits.unreserveMemory(size, cap);
throw x;
}
unsafe.setMemory(base, size, (byte) 0);
if (pa && (base % ps != 0)) {
// Round up to page boundary
address = base + ps - (base & (ps - 1));
} else {
address = base;
}
cleaner = Cleaner.create(this, new Deallocator(base, size, cap));
att = null;
}unsafe.allocateMemory()的源码在openjdk/src/openjdk/hotspot/src/share/vm/prims/unsafe.cpp中。具体的源码如下:
UNSAFE_ENTRY(jlong, Unsafe_AllocateMemory(JNIEnv *env, jobject unsafe, jlong size))
UnsafeWrapper("Unsafe_AllocateMemory");
size_t sz = (size_t)size; if (sz != (julong)size || size < 0) {
THROW_0(vmSymbols::java_lang_IllegalArgumentException());
} if (sz == 0) {return 0;
}
sz = round_to(sz, HeapWordSize); //最后调用的是 u_char* ptr = (u_char*)::malloc(size + space_before + space_after),也就是malloc。
void* x = os::malloc(sz, mtInternal); if (x == NULL) {
THROW_0(vmSymbols::java_lang_OutOfMemoryError());
} //Copy::fill_to_words((HeapWord*)x, sz / HeapWordSize);
return addr_to_java(x);
UNSAFE_ENDJVM通过malloc分配得到连续的缓冲区,这部分缓冲区可以直接作为缓冲区参数进行操作系统调用。
以上就是java之Buffer源码深入分析的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

java怎么学习?java怎么入门?java在哪学?java怎么学才快?不用担心,这里为大家提供了java速学教程(入门到精通),有需要的小伙伴保存下载就能学习啦!

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号